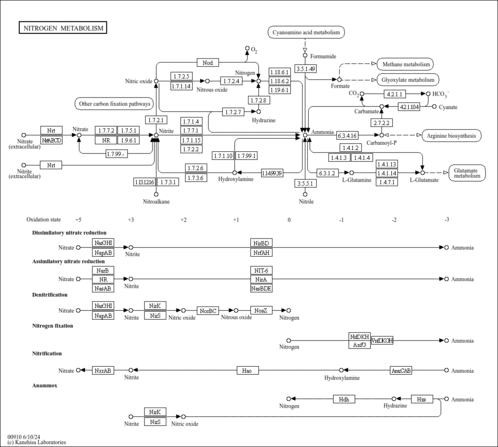
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit beta, mitochondrial | PDHB | 3p21.1-p14.2 | P11177 | details |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, somatic form, mitochondrial | PDHA1 | Xp22.1 | P08559 | details |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, testis-specific form, mitochondrial | PDHA2 | 4q22-q23 | P29803 | details |
| Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial | ALDH6A1 | 14q24.3 | Q02252 | details |
| Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | DLD | 7q31-q32 | P09622 | details |
| Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial | DLAT | 11q23.1 | P10515 | details |
| Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C4 | AKR1C4 | 10p15.1 | P17516 | details |
| 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase [NAD(+)] | HPGD | 4q34-q35 | P15428 | details |
| Tyrosinase | TYR | 11q14-q21 | P14679 | details |
| Aldose reductase | AKR1B1 | 7q35 | P15121 | details |
| Short-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADS | 12q24.31 | P16219 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 1 | MT-ND1 | | P03886 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 1 | NDUFB1 | 14q32.12 | O75438 | details |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 1 | ENPP1 | 6q22-q23 | P22413 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 2, mitochondrial | NDUFS2 | 1q23 | O75306 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 12 | NDUFA12 | 12q22 | Q9UI09 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 3 | CYB5R3 | 22q13.2 | P00387 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 1 | NDUFA1 | | O15239 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 4-like 2 | NDUFA4L2 | 12q13.3 | Q9NRX3 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 3 | NDUFA3 | 19q13.42 | O95167 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 8 | NDUFA8 | 9q33.2 | P51970 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 4 | NDUFA4 | 7p21.3 | O00483 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 4L | MT-ND4L | | P03901 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 11 | NDUFA11 | 19p13.3 | Q86Y39 | details |
| Lathosterol oxidase | SC5DL | 11q23.3 | O75845 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4, mitochondrial | NDUFS4 | 5q11.1 | O43181 | details |
| Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone] | NQO2 | 6p25.2 | P16083 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 5 | MT-ND5 | | P03915 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 3, mitochondrial | NDUFS3 | 11p11.11 | O75489 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 5 | NDUFS5 | 1p34.2-p33 | O43920 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 2, mitochondrial | NDUFV2 | 18p11.22 | P19404 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10, mitochondrial | NDUFA10 | 2q37.3 | O95299 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 6 | NDUFA6 | 22q13.2 | P56556 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 4 | NDUFB4 | 3q13.33 | O95168 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 8, mitochondrial | NDUFS8 | 11q13 | O00217 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 2 | MT-ND2 | | P03891 | details |
| Delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ALDH4A1 | 1p36 | P30038 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 7 | NDUFA7 | 19p13.2 | O95182 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 2 | NDUFA2 | 5q31 | O43678 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial | NDUFS1 | 2q33-q34 | P28331 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 5, mitochondrial | NDUFB5 | 3q26.33 | O43674 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 subunit C2 | NDUFC2 | 11q14.1 | O95298 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 3 | NDUFB3 | 2q31.3 | O43676 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 7 | NDUFB7 | 19p13.12 | P17568 | details |
| Acyl carrier protein, mitochondrial | NDUFAB1 | 16p12.2 | O14561 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 5 | NDUFA5 | 7q32 | Q16718 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 9, mitochondrial | NDUFA9 | 12p13.3 | Q16795 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 4 | MT-ND4 | | P03905 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 7, mitochondrial | NDUFS7 | 19p13.3 | O75251 | details |
| Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase | XDH | 2p23.1 | P47989 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 3 | MT-ND3 | | P03897 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial | NDUFV1 | 11q13 | P49821 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 9 | NDUFB9 | 8q13.3 | Q9Y6M9 | details |
| Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | MTHFR | 1p36.3 | P42898 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 6 | MT-ND6 | | P03923 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 13 | NDUFA13 | 19p13.2 | Q9P0J0 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 6, mitochondrial | NDUFS6 | 5p15.33 | O75380 | details |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3 | ENPP3 | 6q22 | O14638 | details |
| Glutathione reductase, mitochondrial | GSR | 8p21.1 | P00390 | details |
| Retinal dehydrogenase 1 | ALDH1A1 | 9q21.13 | P00352 | details |
| Retinal dehydrogenase 2 | ALDH1A2 | 15q21.3 | O94788 | details |
| Deoxyhypusine synthase | DHPS | 19p13.2 | P49366 | details |
| Succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ALDH5A1 | 6p22 | P51649 | details |
| Squalene synthase | FDFT1 | 8p23.1-p22 | P37268 | details |
| Methylsterol monooxygenase 1 | MSMO1 | 4q32-q34 | Q15800 | details |
| Sterol-4-alpha-carboxylate 3-dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | NSDHL | Xq28 | Q15738 | details |
| 4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH9A1 | 1q23.1 | P49189 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase, dimeric NADP-preferring | ALDH3A1 | 17p11.2 | P30838 | details |
| Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH7A1 | 5q31 | P49419 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 | ALDH1A3 | 15q26.3 | P47895 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ALDH2 | 12q24.2 | P05091 | details |
| Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH3A2 | 17p11.2 | P51648 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase X, mitochondrial | ALDH1B1 | 9p11.1 | P30837 | details |
| Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1, mitochondrial | PYCR1 | 17q25.3 | P32322 | details |
| Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 2 | PYCR2 | 1q42.12 | Q96C36 | details |
| Kynureninase | KYNU | 2q22.2 | Q16719 | details |
| Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase 1 | NMNAT1 | 1p36.22 | Q9HAN9 | details |
| Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase 3 | NMNAT3 | 3q23 | Q96T66 | details |
| Nicotinate-nucleotide pyrophosphorylase [carboxylating] | QPRT | 16p11.2 | Q15274 | details |
| Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase 2 | NMNAT2 | 1q25 | Q9BZQ4 | details |
| Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C3 | AKR1C3 | 10p15-p14 | P42330 | details |
| 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 | HSD17B10 | Xp11.2 | Q99714 | details |
| Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | HADH | 4q22-q26 | Q16836 | details |
| GDP-mannose 4,6 dehydratase | GMDS | 6p25 | O60547 | details |
| Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 | AKR1C1 | 10p15-p14 | Q04828 | details |
| Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C2 | AKR1C2 | 10p15-p14 | P52895 | details |
| Glyoxylate reductase/hydroxypyruvate reductase | GRHPR | 9q12 | Q9UBQ7 | details |
| 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | HIBADH | 7p15.2 | P31937 | details |
| 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | OGDH | 7p14-p13 | Q02218 | details |
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 2 | HSD17B2 | 16q24.1-q24.2 | P37059 | details |
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 8 | HSD17B8 | 6p21.3 | Q92506 | details |
| 11-cis retinol dehydrogenase | RDH5 | 12q13-q14 | Q92781 | details |
| Sorbitol dehydrogenase | SORD | 15q15.3 | Q00796 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase [NADP(+)] | AKR1A1 | 1p33-p32 | P14550 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase 4 | ADH4 | 4q22 | P08319 | details |
| D-beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | BDH1 | 3q29 | Q02338 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 3 member B2 | ALDH3B2 | 11q13 | P48448 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 3 member B1 | ALDH3B1 | 11q13 | P43353 | details |
| Dihydropteridine reductase | QDPR | 4p15.31 | P09417 | details |
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 11 | HSD17B11 | 4q22.1 | Q8NBQ5 | details |
| 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase | DHCR7 | 11q13.4 | Q9UBM7 | details |
| Putative adenosylhomocysteinase 3 | AHCYL2 | 7q32.1 | Q96HN2 | details |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | AHCY | 20q11.22 | P23526 | details |
| Putative adenosylhomocysteinase 2 | AHCYL1 | 1p13.2 | O43865 | details |
| Glutamate dehydrogenase 2, mitochondrial | GLUD2 | Xq24-q25 | P49448 | details |
| Aminomethyltransferase, mitochondrial | AMT | 3p21.2-p21.1 | P48728 | details |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, testis-specific | GAPDHS | 19q13.12 | O14556 | details |
| Glutamate dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | GLUD1 | 10q23.3 | P00367 | details |
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GAPDH | 12p13 | P04406 | details |
| Biliverdin reductase A | BLVRA | 7p13 | P53004 | details |
| Flavin reductase (NADPH) | BLVRB | 19q13.1-q13.2 | P30043 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 7 | ADCY7 | 16q12.1 | P51828 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 4 | ADCY4 | 14q12 | Q8NFM4 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 6 | ADCY6 | 12q12-q13 | O43306 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 5 | ADCY5 | 3q21.1 | O95622 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 8 | ADCY8 | 8q24 | P40145 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 9 | ADCY9 | 16p13.3 | O60503 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 3 | ADCY3 | 2p23.3 | O60266 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 1 | ADCY1 | 7p13-p12 | Q08828 | details |
| Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 | HSD11B2 | 16q22 | P80365 | details |
| Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1 | HSD11B1 | 1q32-q41 | P28845 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 | ADH5 | 4q23 | P11766 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase 1B | ADH1B | 4q23 | P00325 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase class 4 mu/sigma chain | ADH7 | 4q23-q24 | P40394 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase 1A | ADH1A | 4q23 | P07327 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase 6 | ADH6 | 4q23 | P28332 | details |
| Alcohol dehydrogenase 1C | ADH1C | 4q23 | P00326 | details |
| Dihydrofolate reductase | DHFR | 5q11.2-q13.2 | P00374 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase [NAD(+)], cytoplasmic | GPD1 | 12q12-q13 | P21695 | details |
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 1 | HSD17B1 | 17q11-q21 | P14061 | details |
| 3-keto-steroid reductase | HSD17B7 | 1q23 | P56937 | details |
| Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde synthase, mitochondrial | AASS | 7q31.3 | Q9UDR5 | details |
| Malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | MDH2 | 7cen-q22 | P40926 | details |
| Malate dehydrogenase, cytoplasmic | MDH1 | 2p13.3 | P40925 | details |
| Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 | IMPDH2 | 3p21.2 | P12268 | details |
| Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase 1 | IMPDH1 | 7q31.3-q32 | P20839 | details |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase A-like 6A | LDHAL6A | 11p15.1 | Q6ZMR3 | details |
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit beta, mitochondrial | IDH3B | 20p13 | O43837 | details |
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit alpha, mitochondrial | IDH3A | 15q25.1-q25.2 | P50213 | details |
| Isocitrate dehydrogenase [NAD] subunit gamma, mitochondrial | IDH3G | Xq28 | P51553 | details |
| Tankyrase-2 | TNKS2 | 10q23.3 | Q9H2K2 | details |
| dTDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydratase | TGDS | 13q32.1 | O95455 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-6 | SIRT6 | 19p13.3 | Q8N6T7 | details |
| UDP-glucose 4-epimerase | GALE | 1p36-p35 | Q14376 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 3 | PARP3 | 3p21.31-p21.1 | Q9Y6F1 | details |
| Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 3 | ART3 | 4p15.1-p14 | Q13508 | details |
| UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase | UGDH | 4p15.1 | O60701 | details |
| Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 5 | ART5 | 11p15.4 | Q96L15 | details |
| GPI-linked NAD(P)(+)--arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 | ART1 | 11p15 | P52961 | details |
| NAD(P) transhydrogenase, mitochondrial | NNT | 5p12 | Q13423 | details |
| Tankyrase-1 | TNKS | 8p23.1 | O95271 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | PARP1 | 1q41-q42 | P09874 | details |
| Urocanate hydratase | UROC1 | 3q21.3 | Q96N76 | details |
| ADP-ribosyl cyclase 2 | BST1 | 4p15 | Q10588 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2 | PARP2 | 14q11.2-q12 | Q9UGN5 | details |
| NAD kinase | NADK | 1p36.33 | O95544 | details |
| ADP-ribosyl cyclase 1 | CD38 | 4p15 | P28907 | details |
| Ecto-ADP-ribosyltransferase 4 | ART4 | 12p13-p12 | Q93070 | details |
| Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial | MTHFD2 | 2p13.1 | P13995 | details |
| Adenylate cyclase type 2 | ADCY2 | 5p15.3 | Q08462 | details |
| D-3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase | PHGDH | 1p12 | O43175 | details |
| C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase, cytoplasmic | MTHFD1 | 14q24 | P11586 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 4 | PARP4 | 13q11 | Q9UKK3 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 11, mitochondrial | NDUFB11 | | Q9NX14 | details |
| Prostaglandin reductase 1 | PTGR1 | 9q31.3 | Q14914 | details |
| NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 | NQO1 | 16q22.1 | P15559 | details |
| Proline dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | PRODH | 22q11.21 | O43272 | details |
| Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase | KMO | 1q42-q44 | O15229 | details |
| 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 6 | HSD17B6 | 12q13 | O14756 | details |
| Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 3 | PYCRL | 8q24.3 | Q53H96 | details |
| Retinol dehydrogenase 16 | RDH16 | 12q13.3 | O75452 | details |
| Glycine cleavage system H protein, mitochondrial | GCSH | | P23434 | details |
| Dual oxidase 2 | DUOX2 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD8 | details |
| UDP-glucuronic acid decarboxylase 1 | UXS1 | 2q12.2 | Q8NBZ7 | details |
| Glutamine-dependent NAD(+) synthetase | NADSYN1 | 11q13.4 | Q6IA69 | details |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase B chain | LDHB | 12p12.2-p12.1 | P07195 | details |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase C chain | LDHC | 11p15.1 | P07864 | details |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase A chain | LDHA | 11p15.4 | P00338 | details |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase A-like 6B | LDHAL6B | 15q22.2 | Q9BYZ2 | details |
| Nicotinamide riboside kinase 1 | NMRK1 | 9q21.13 | Q9NWW6 | details |
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Delta 5-->4-isomerase type 1 | HSD3B1 | 1p13.1 | P14060 | details |
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Delta 5-->4-isomerase type 2 | HSD3B2 | 1p13.1 | P26439 | details |
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 7 | HSD3B7 | 16p11.2 | Q9H2F3 | details |
| Inositol-3-phosphate synthase 1 | ISYNA1 | 19p13.11 | Q9NPH2 | details |
| Dual oxidase 1 | DUOX1 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD9 | details |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase type 2 | BDH2 | 4q24 | Q9BUT1 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like protein | GPD1L | 3p22.3 | Q8N335 | details |
| Probable bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase 2 | MTHFD2L | 4q13.3 | Q9H903 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 1 | CYB5R1 | 1q32.1 | Q9UHQ9 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 2 | CYB5R2 | 11p15.4 | Q6BCY4 | details |
| Cytochrome b5 reductase 4 | CYB5R4 | 6pter-q22.33 | Q7L1T6 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase-like | CYB5RL | 1p32.3 | Q6IPT4 | details |
| Probable saccharopine dehydrogenase | SCCPDH | 1q44 | Q8NBX0 | details |
| Methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase (NADP+ dependent) 2, methenyltetrahydrofolate cyclohydrolase | MTHFD2 | 2p13.1 | Q7Z650 | details |
| Kynurenine formamidase | AFMID | 17q25.3 | Q63HM1 | details |
| Acyl-CoA synthetase family member 4 | AASDH | 4q12 | Q4L235 | details |
| Aminoadipate-semialdehyde synthase | AASS | 7q31.3 | A4D0W4 | details |
| Peroxisomal NADH pyrophosphatase NUDT12 | NUDT12 | 5q21.2 | Q9BQG2 | details |
| Inosine-5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase | IMPDH1 | 7q31.3-q32 | A4D0Z6 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP3 | STEAP3 | 2q14.2 | Q658P3 | details |
| All-trans-retinol 13,14-reductase | RETSAT | 2p11.2 | Q6NUM9 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP1 | STEAP1 | 7q21 | Q9UHE8 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP2 | STEAP2 | 7q21 | Q8NFT2 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP4 | STEAP4 | 7q21.12 | Q687X5 | details |
| Peroxisomal coenzyme A diphosphatase NUDT7 | NUDT7 | 16q23.1 | P0C024 | details |
| Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 8 member A1 | ALDH8A1 | 6q23.2 | Q9H2A2 | details |
| Putative L-aspartate dehydrogenase | ASPDH | 19q13.33 | A6ND91 | details |
| Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 12 | HSD17B12 | 11p11.2 | Q53GQ0 | details |
| 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 14 | HSD17B14 | 19q13.33 | Q9BPX1 | details |
| Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase | NAMPT | 7q22.3 | P43490 | details |
| Nicotinamide riboside kinase 2 | NMRK2 | 19p13.3 | Q9NPI5 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 10 | PARP10 | 8q24.3 | Q53GL7 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 11 | PARP11 | 12p13.3 | Q9NR21 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 12 | PARP12 | 7q34 | Q9H0J9 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 14 | PARP14 | 3q21.1 | Q460N5 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 15 | PARP15 | 3q21.1 | Q460N3 | details |
| Mono [ADP-ribose] polymerase PARP16 | PARP16 | 15q22.31 | Q8N5Y8 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 6 | PARP6 | 15q23 | Q2NL67 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 8 | PARP8 | 5q11.1 | Q8N3A8 | details |
| Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 9 | PARP9 | 3q21 | Q8IXQ6 | details |
| TCDD-inducible poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase | TIPARP | 3q25.31 | Q7Z3E1 | details |
| Nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase | NAPRT1 | 8q24.3 | Q6XQN6 | details |
| Prostaglandin reductase 2 | PTGR2 | 14q24.3 | Q8N8N7 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | SIRT1 | 10q21.3 | Q96EB6 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 | SIRT2 | 19q13 | Q8IXJ6 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3, mitochondrial | SIRT3 | 11p15.5 | Q9NTG7 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-4 | SIRT4 | 12q | Q9Y6E7 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5, mitochondrial | SIRT5 | 6p23 | Q9NXA8 | details |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-7 | SIRT7 | 17q25 | Q9NRC8 | details |
| tRNA 2'-phosphotransferase 1 | TRPT1 | 11q13.1 | Q86TN4 | details |
| 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase-like, mitochondrial | OGDHL | | Q9ULD0 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 2, 8kDa | NDUFB2 | 7q34 | A4D1T5 | details |
| L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase-phosphopantetheinyl transferase | AASDHPPT | 11q22 | Q9NRN7 | details |
| 14 kDa phosphohistidine phosphatase | PHPT1 | | Q9NRX4 | details |
| Aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 | AKR1B10 | | O60218 | details |
| Dihydrofolate reductase, mitochondrial | DHFRL1 | 3q11.1 | Q86XF0 | details |
| NAD kinase domain-containing protein 1, mitochondrial | NADKD1 | 5p13.2 | Q4G0N4 | details |
| Epidermal retinol dehydrogenase 2 | SDR16C5 | 8q12.1 | Q8N3Y7 | details |