| Tyrosinase | TYR | 11q14-q21 | P14679 | details |
| Peroxisomal sarcosine oxidase | PIPOX | 17q11.2 | Q9P0Z9 | details |
| Peroxisomal N(1)-acetyl-spermine/spermidine oxidase | PAOX | 10q26.3 | Q6QHF9 | details |
| Aldehyde oxidase | AOX1 | 2q33 | Q06278 | details |
| Lathosterol oxidase | SC5DL | 11q23.3 | O75845 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 5 | FMO5 | 1q21.1 | P49326 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 | ACOX1 | 17q25.1 | Q15067 | details |
| D-aspartate oxidase | DDO | 6q21 | Q99489 | details |
| Heme oxygenase 2 | HMOX2 | 16p13.3 | P30519 | details |
| Squalene monooxygenase | SQLE | 8q24.1 | Q14534 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 2 | FMO2 | 1q24.3 | Q99518 | details |
| Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B | MAOB | Xp11.23 | P27338 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 4 | FMO4 | 1q24.3 | P31512 | details |
| Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] A | MAOA | Xp11.3 | P21397 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3 | FMO3 | 1q24.3 | P31513 | details |
| Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase | XDH | 2p23.1 | P47989 | details |
| Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial | DHODH | 16q22 | Q02127 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 1 | FMO1 | 1q24.3 | Q01740 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 3 | ACOX3 | 4p15.3 | O15254 | details |
| Heme oxygenase 1 | HMOX1 | 22q13.1 | P09601 | details |
| D-amino-acid oxidase | DAO | 12q24 | P14920 | details |
| Coproporphyrinogen-III oxidase, mitochondrial | CPOX | 3q12 | P36551 | details |
| Peptidyl-glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase | PAM | 5q14-q21 | P19021 | details |
| Dopamine beta-hydroxylase | DBH | 9q34 | P09172 | details |
| Methylsterol monooxygenase 1 | MSMO1 | 4q32-q34 | Q15800 | details |
| Sterol-4-alpha-carboxylate 3-dehydrogenase, decarboxylating | NSDHL | Xq28 | Q15738 | details |
| Lanosterol 14-alpha demethylase | CYP51A1 | 7q21.2 | Q16850 | details |
| Phytanoyl-CoA dioxygenase, peroxisomal | PHYH | 10p13 | O14832 | details |
| Tyrosine 3-monooxygenase | TH | 11p15.5 | P07101 | details |
| Phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase | PAH | 12q22-q24.2 | P00439 | details |
| Peroxiredoxin-6 | PRDX6 | 1q25.1 | P30041 | details |
| Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-2 | P4HA2 | 5q31 | O15460 | details |
| Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-1 | P4HA1 | 10q21.3-q23.1 | P13674 | details |
| Acyl-CoA desaturase | SCD | 10q24.31 | O00767 | details |
| Gamma-butyrobetaine dioxygenase | BBOX1 | 11p14.2 | O75936 | details |
| Amiloride-sensitive amine oxidase [copper-containing] | ABP1 | 7q36.1 | P19801 | details |
| Membrane primary amine oxidase | AOC3 | 17q21 | Q16853 | details |
| Retina-specific copper amine oxidase | AOC2 | 17q21 | O75106 | details |
| Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 | IDO1 | 8p12-p11 | P14902 | details |
| Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 | PLOD1 | 1p36.22 | Q02809 | details |
| Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 2 | PLOD2 | 3q24 | O00469 | details |
| Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 3 | PLOD3 | 7q22 | O60568 | details |
| Tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 1 | TPH1 | 11p15.3-p14 | P17752 | details |
| Tryptophan 5-hydroxylase 2 | TPH2 | 12q21.1 | Q8IWU9 | details |
| Cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase | CYP7A1 | 8q11-q12 | P22680 | details |
| Pyridoxine-5'-phosphate oxidase | PNPO | 17q21.32 | Q9NVS9 | details |
| Protein-lysine 6-oxidase | LOX | 5q23.2 | P28300 | details |
| Hydroxyacid oxidase 1 | HAO1 | 20p12 | Q9UJM8 | details |
| Hydroxyacid oxidase 2 | HAO2 | 1p13.3-p13.1 | Q9NYQ3 | details |
| Inositol oxygenase | MIOX | 22q13.3 | Q9UGB7 | details |
| 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase | HPD | 12q24-qter | P32754 | details |
| Homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase | HGD | 3q13.33 | Q93099 | details |
| 3-keto-steroid reductase | HSD17B7 | 1q23 | P56937 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, inducible | NOS2 | 17q11.2-q12 | P35228 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, brain | NOS1 | 12q24.2-q24.31 | P29475 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | NOS3 | 7q36 | P29474 | details |
| Cysteine dioxygenase type 1 | CDO1 | 5q23.2 | Q16878 | details |
| Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | ALOX5 | 10q11.2 | P09917 | details |
| Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase B | ALOX15B | 17p13.1 | O15296 | details |
| Arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, 12S-type | ALOX12 | 17p13.1 | P18054 | details |
| Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | PTGS2 | 1q25.2-q25.3 | P35354 | details |
| Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 | PTGS1 | 9q32-q33.3 | P23219 | details |
| Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase | ALOX15 | 17p13.3 | P16050 | details |
| Leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 1 | CYP4F2 | 19p13.12 | P78329 | details |
| Leukotriene-B(4) omega-hydroxylase 2 | CYP4F3 | 19p13.2 | Q08477 | details |
| Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | PPOX | 1q22 | P50336 | details |
| Aspartyl/asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase | ASPH | 8q12.1 | Q12797 | details |
| Sterol 26-hydroxylase, mitochondrial | CYP27A1 | 2q33-qter | Q02318 | details |
| 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1 alpha hydroxylase, mitochondrial | CYP27B1 | 12q13.1-q13.3 | O15528 | details |
| Steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase | CYP17A1 | 10q24.3 | P05093 | details |
| Sulfite oxidase, mitochondrial | SUOX | 12q13.2 | P51687 | details |
| 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase | HAAO | 2p21 | P46952 | details |
| Beta,beta-carotene 15,15'-monooxygenase | BCMO1 | 16q23.2 | Q9HAY6 | details |
| Catalase | CAT | 11p13 | P04040 | details |
| 25-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase | CYP7B1 | 8q21.3 | O75881 | details |
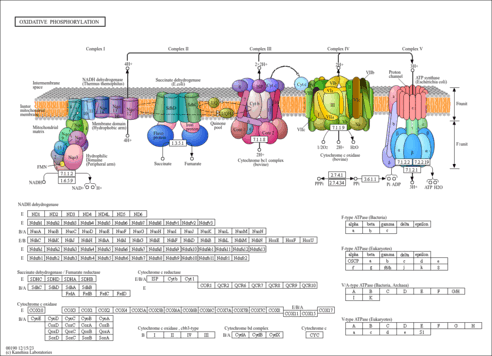
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 | MT-CO1 | | P00395 | details |
| Vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase | GGCX | 2p12 | P38435 | details |
| 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) 24-hydroxylase, mitochondrial | CYP24A1 | 20q13 | Q07973 | details |
| Putative dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 6 | FMO6P | | O60774 | details |
| Superoxide dismutase [Mn], mitochondrial | SOD2 | 6q25.3 | P04179 | details |
| Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | SOD1 | 21q22.11 | P00441 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A1, mitochondrial | COX7A1 | 19q13.1 | P24310 | details |
| Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase | KMO | 1q42-q44 | O15229 | details |
| Spermine oxidase | SMOX | 20p13 | Q9NWM0 | details |
| Vitamin D 25-hydroxylase | CYP2R1 | 11p15.2 | Q6VVX0 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A2, mitochondrial | COX7A2 | 6q12 | P14406 | details |
| Cholesterol 25-hydroxylase | CH25H | 10q23 | O95992 | details |
| Dual oxidase 2 | DUOX2 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD8 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6A2, mitochondrial | COX6A2 | 16p | Q02221 | details |
| Extracellular superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | SOD3 | 4p15.2 | P08294 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7B, mitochondrial | COX7B | | P24311 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7C, mitochondrial | COX7C | 5q14 | P15954 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 5B, mitochondrial | COX5B | 2cen-q13 | P10606 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B1 | COX6B1 | 19q13.1 | P14854 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7B2, mitochondrial | COX7B2 | 4p12 | Q8TF08 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 1, mitochondrial | COX4I1 | 16q24.1 | P13073 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6B2 | COX6B2 | 19q13.42 | Q6YFQ2 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 8A, mitochondrial | COX8A | 11q12-q13 | P10176 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C | COX6C | 8q22.2 | P09669 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A-related protein, mitochondrial | COX7A2L | 2p21 | O14548 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 8C, mitochondrial | COX8C | 14q32.12 | Q7Z4L0 | details |
| Trimethyllysine dioxygenase, mitochondrial | TMLHE | Xq28 | Q9NVH6 | details |
| Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase | CYP46A1 | 14q32.1 | Q9Y6A2 | details |
| Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase | TDO2 | 4q31-q32 | P48775 | details |
| 24-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase | CYP39A1 | 6p21.1-p11.2 | Q9NYL5 | details |
| 7-alpha-hydroxycholest-4-en-3-one 12-alpha-hydroxylase | CYP8B1 | 3p22.1 | Q9UNU6 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2 | MT-CO2 | | P00403 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6A1, mitochondrial | COX6A1 | 12q24.2|12q24.2 | P12074 | details |
| Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4 isoform 2, mitochondrial | COX4I2 | 20q11.21 | Q96KJ9 | details |
| Dual oxidase 1 | DUOX1 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD9 | details |
| Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 5 | SCD5 | 4q21.22 | Q86SK9 | details |
| Putative uncharacterized protein DKFZp686B0215 | DKFZp686B0215 | | Q5HYI4 | details |
| Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 | IDO2 | 8p11.21 | Q6ZQW0 | details |
| Cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 | CYP1A1 | 15q24.1 | A0N0X8 | details |
| Ubiquinone biosynthesis monooxygenase COQ6 | COQ6 | | Q9Y2Z9 | details |
| Lysyl oxidase homolog 2 | LOXL2 | 8p21.3 | Q9Y4K0 | details |
| FAD-linked sulfhydryl oxidase ALR | GFER | 16p13.3-p13.12 | P55789 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL1 | MICAL1 | 6q21 | Q8TDZ2 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL2 | MICAL2 | 11p15.3 | O94851 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL3 | MICAL3 | 22q11.21 | Q7RTP6 | details |
| L-amino-acid oxidase | IL4I1 | 19q13.3-q13.4 | Q96RQ9 | details |
| Prenylcysteine oxidase 1 | PCYOX1 | 2p13.3 | Q9UHG3 | details |
| Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 | QSOX1 | 1q24 | O00391 | details |
| Sulfhydryl oxidase 2 | QSOX2 | 9q34.3 | Q6ZRP7 | details |
| 2-aminoethanethiol dioxygenase | ADO | 10q21.3 | Q96SZ5 | details |
| Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase alkB homolog 2 | ALKBH2 | 12q24.11 | Q6NS38 | details |
| Beta,beta-carotene 9',10'-oxygenase | BCO2 | 11q23.1 | Q9BYV7 | details |
| Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 1 | LEPRE1 | 1p34.1 | Q32P28 | details |
| Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 2 | LEPREL1 | 3q28 | Q8IVL5 | details |
| Prolyl 3-hydroxylase 3 | LEPREL2 | 12q13 | Q8IVL6 | details |
| Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-3 | P4HA3 | 11q13.4 | Q7Z4N8 | details |
| Lysine-specific demethylase 2A | KDM2A | 11q13.2 | Q9Y2K7 | details |
| Lysine-specific demethylase 2B | KDM2B | 12q24.31 | Q8NHM5 | details |
| Deoxyhypusine hydroxylase | DOHH | 19p13.3 | Q9BU89 | details |
| Egl nine homolog 1 | EGLN1 | 1q42.1 | Q9GZT9 | details |
| Egl nine homolog 2 | EGLN2 | 19q13.2 | Q96KS0 | details |
| Egl nine homolog 3 | EGLN3 | 14q13.1 | Q9H6Z9 | details |
| Transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase | P4HTM | 3p21.3 | Q9NXG6 | details |
| Cytochrome P450, family 21, subfamily A, polypeptide 2 | CYP21A2 | 6p21.3 | Q08AG9 | details |
| CP protein | CP | 3q23-q25 | A5PL27 | details |
| NOS1 mutant | NOS1 | 12q24.2-q24.31 | B3VK56 | details |
| 1,2-dihydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentene dioxygenase | ADI1 | 2p25.3 | Q9BV57 | details |
| Alkylglycerol monooxygenase | AGMO | 7p21.2 | Q6ZNB7 | details |
| Steroid 21-hydroxylase | CYP21A2 | 6p21.3 | P08686 | details |
| Lysine-specific demethylase 8 | KDM8 | 16p12.1 | Q8N371 | details |
| Bifunctional lysine-specific demethylase and histidyl-hydroxylase MINA | MINA | 3q11.2 | Q8IUF8 | details |
| Bifunctional lysine-specific demethylase and histidyl-hydroxylase NO66 | NO66 | 14q24.3 | Q9H6W3 | details |
| Histone lysine demethylase PHF8 | PHF8 | Xp11.22 | Q9UPP1 | details |
| Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET1 | TET1 | 10q21 | Q8NFU7 | details |
| Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET2 | TET2 | 4q24 | Q6N021 | details |
| Methylcytosine dioxygenase TET3 | TET3 | 2p13.1 | O43151 | details |