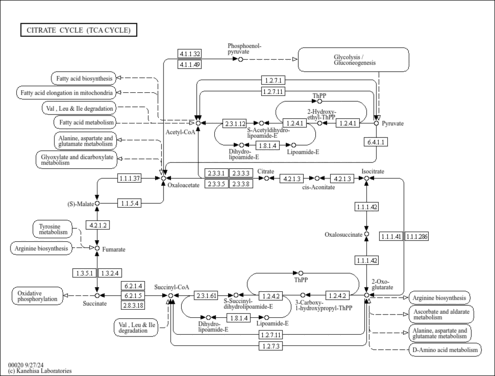
| Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | DLD | 7q31-q32 | P09622 | details |
| Long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADL | 2q34 | P28330 | details |
| Short-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADS | 12q24.31 | P16219 | details |
| Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADM | 1p31 | P11310 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 1 | MT-ND1 | | P03886 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 1 | NDUFB1 | 14q32.12 | O75438 | details |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 1 | ENPP1 | 6q22-q23 | P22413 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 2, mitochondrial | NDUFS2 | 1q23 | O75306 | details |
| Succinate dehydrogenase cytochrome b560 subunit, mitochondrial | SDHC | 1q23.3 | Q99643 | details |
| Peroxisomal sarcosine oxidase | PIPOX | 17q11.2 | Q9P0Z9 | details |
| Peroxisomal N(1)-acetyl-spermine/spermidine oxidase | PAOX | 10q26.3 | Q6QHF9 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 12 | NDUFA12 | 12q22 | Q9UI09 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 3 | CYB5R3 | 22q13.2 | P00387 | details |
| Aldehyde oxidase | AOX1 | 2q33 | Q06278 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 1 | NDUFA1 | | O15239 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 4-like 2 | NDUFA4L2 | 12q13.3 | Q9NRX3 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 3 | NDUFA3 | 19q13.42 | O95167 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 8 | NDUFA8 | 9q33.2 | P51970 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 4 | NDUFA4 | 7p21.3 | O00483 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 4L | MT-ND4L | | P03901 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 11 | NDUFA11 | 19p13.3 | Q86Y39 | details |
| Thioredoxin reductase 1, cytoplasmic | TXNRD1 | 12q23-q24.1 | Q16881 | details |
| Lathosterol oxidase | SC5DL | 11q23.3 | O75845 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4, mitochondrial | NDUFS4 | 5q11.1 | O43181 | details |
| Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone] | NQO2 | 6p25.2 | P16083 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 3, mitochondrial | NDUFS3 | 11p11.11 | O75489 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 5 | NDUFS5 | 1p34.2-p33 | O43920 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 2, mitochondrial | NDUFV2 | 18p11.22 | P19404 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 5 | FMO5 | 1q21.1 | P49326 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 10, mitochondrial | NDUFA10 | 2q37.3 | O95299 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 6 | NDUFA6 | 22q13.2 | P56556 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 | ACOX1 | 17q25.1 | Q15067 | details |
| D-aspartate oxidase | DDO | 6q21 | Q99489 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 4 | NDUFB4 | 3q13.33 | O95168 | details |
| Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit, mitochondrial | SDHA | 5p15 | P31040 | details |
| Heme oxygenase 2 | HMOX2 | 16p13.3 | P30519 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 8, mitochondrial | NDUFS8 | 11q13 | O00217 | details |
| Squalene monooxygenase | SQLE | 8q24.1 | Q14534 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 2 | MT-ND2 | | P03891 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 2 | FMO2 | 1q24.3 | Q99518 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 7 | NDUFA7 | 19p13.2 | O95182 | details |
| Thioredoxin reductase 2, mitochondrial | TXNRD2 | 22q11.21 | Q9NNW7 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 2 | NDUFA2 | 5q31 | O43678 | details |
| Methionine synthase | MTR | 1q43 | Q99707 | details |
| Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B | MAOB | Xp11.23 | P27338 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 75 kDa subunit, mitochondrial | NDUFS1 | 2q33-q34 | P28331 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 5, mitochondrial | NDUFB5 | 3q26.33 | O43674 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 2 | ACOX2 | 3p14.3 | Q99424 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 4 | FMO4 | 1q24.3 | P31512 | details |
| Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | IVD | 15q14-q15 | P26440 | details |
| Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] A | MAOA | Xp11.3 | P21397 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 subunit C2 | NDUFC2 | 11q14.1 | O95298 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 3 | FMO3 | 1q24.3 | P31513 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 3 | NDUFB3 | 2q31.3 | O43676 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 7 | NDUFB7 | 19p13.12 | P17568 | details |
| Acyl carrier protein, mitochondrial | NDUFAB1 | 16p12.2 | O14561 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 5 | NDUFA5 | 7q32 | Q16718 | details |
| Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase, mitochondrial | ETFDH | 4q32-q35 | Q16134 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 9, mitochondrial | NDUFA9 | 12p13.3 | Q16795 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 4 | MT-ND4 | | P03905 | details |
| Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] cytochrome b small subunit, mitochondrial | SDHD | 11q23 | O14521 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 7, mitochondrial | NDUFS7 | 19p13.3 | O75251 | details |
| Xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase | XDH | 2p23.1 | P47989 | details |
| NADPH--cytochrome P450 reductase | POR | 7q11.2 | P16435 | details |
| Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial | DHODH | 16q22 | Q02127 | details |
| Dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 1 | FMO1 | 1q24.3 | Q01740 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial | NDUFV1 | 11q13 | P49821 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 9 | NDUFB9 | 8q13.3 | Q9Y6M9 | details |
| Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase | MTHFR | 1p36.3 | P42898 | details |
| NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 6 | MT-ND6 | | P03923 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex subunit 13 | NDUFA13 | 19p13.2 | Q9P0J0 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 6, mitochondrial | NDUFS6 | 5p15.33 | O75380 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 3 | ACOX3 | 4p15.3 | O15254 | details |
| Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur subunit, mitochondrial | SDHB | 1p36.1-p35 | P21912 | details |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3 | ENPP3 | 6q22 | O14638 | details |
| Glutathione reductase, mitochondrial | GSR | 8p21.1 | P00390 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | GPD2 | 2q24.1 | P43304 | details |
| Heme oxygenase 1 | HMOX1 | 22q13.1 | P09601 | details |
| Retinal dehydrogenase 1 | ALDH1A1 | 9q21.13 | P00352 | details |
| Choline dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | CHDH | 3p21.1 | Q8NE62 | details |
| Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | GCDH | 19p13.2 | Q92947 | details |
| Dimethylglycine dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | DMGDH | 5q14.1 | Q9UI17 | details |
| NADPH:adrenodoxin oxidoreductase, mitochondrial | FDXR | 17q24-q25 | P22570 | details |
| Retinal dehydrogenase 2 | ALDH1A2 | 15q21.3 | O94788 | details |
| D-amino-acid oxidase | DAO | 12q24 | P14920 | details |
| Methionine synthase reductase | MTRR | 5p15.31 | Q9UBK8 | details |
| tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 2-like | DUS2L | 16q22.1 | Q9NX74 | details |
| Flavin reductase (NADPH) | BLVRB | 19q13.1-q13.2 | P30043 | details |
| Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)] | DPYD | 1p22 | Q12882 | details |
| Sarcosine dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | SARDH | 9q33-q34 | Q9UL12 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, inducible | NOS2 | 17q11.2-q12 | P35228 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, brain | NOS1 | 12q24.2-q24.31 | P29475 | details |
| Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | NOS3 | 7q36 | P29474 | details |
| Protoporphyrinogen oxidase | PPOX | 1q22 | P50336 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 11, mitochondrial | NDUFB11 | | Q9NX14 | details |
| Alkyldihydroxyacetonephosphate synthase, peroxisomal | AGPS | 2q31.2 | O00116 | details |
| Short/branched chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADSB | 10q26.13 | P45954 | details |
| NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 | NQO1 | 16q22.1 | P15559 | details |
| Putative dimethylaniline monooxygenase [N-oxide-forming] 6 | FMO6P | | O60774 | details |
| Delta(24)-sterol reductase | DHCR24 | 1p32.3 | Q15392 | details |
| Proline dehydrogenase 1, mitochondrial | PRODH | 22q11.21 | O43272 | details |
| D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | D2HGDH | 2q37.3 | Q8N465 | details |
| L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | L2HGDH | 14q21.3 | Q9H9P8 | details |
| Bifunctional ATP-dependent dihydroxyacetone kinase/FAD-AMP lyase (cyclizing) | DAK | 11q12.2 | Q3LXA3 | details |
| Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase | KMO | 1q42-q44 | O15229 | details |
| Spermine oxidase | SMOX | 20p13 | Q9NWM0 | details |
| Dual oxidase 2 | DUOX2 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD8 | details |
| Probable D-lactate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | LDHD | 16q23.1 | Q86WU2 | details |
| Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACAD8 | 11q25 | Q9UKU7 | details |
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 9, mitochondrial | ACAD9 | 3q21.3 | Q9H845 | details |
| Probable proline dehydrogenase 2 | PRODH2 | 19q13.1 | Q9UF12 | details |
| Dual oxidase 1 | DUOX1 | 15q15.3 | Q9NRD9 | details |
| Thioredoxin reductase 3 | TXNRD3 | 3q21.3 | Q86VQ6 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 1 | CYB5R1 | 1q32.1 | Q9UHQ9 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase 2 | CYB5R2 | 11p15.4 | Q6BCY4 | details |
| Cytochrome b5 reductase 4 | CYB5R4 | 6pter-q22.33 | Q7L1T6 | details |
| NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase-like | CYB5RL | 1p32.3 | Q6IPT4 | details |
| Putative uncharacterized protein DKFZp686B0215 | DKFZp686B0215 | | Q5HYI4 | details |
| FAD synthase | FLAD1 | 1q21.3 | Q8NFF5 | details |
| Ubiquinone biosynthesis monooxygenase COQ6 | COQ6 | | Q9Y2Z9 | details |
| NADPH oxidase 5 | NOX5 | 15q23 | Q96PH1 | details |
| NADPH oxidase 3 | NOX3 | 6q25.3 | Q9HBY0 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP3 | STEAP3 | 2q14.2 | Q658P3 | details |
| Very long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADVL | 17p13.1 | P49748 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A oxidase-like protein | ACOXL | 2q13 | Q9NUZ1 | details |
| FAD-linked sulfhydryl oxidase ALR | GFER | 16p13.3-p13.12 | P55789 | details |
| Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1B | KDM1B | 6p22.3 | Q8NB78 | details |
| tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 1-like | DUS1L | 17q25.3 | Q6P1R4 | details |
| tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 3-like | DUS3L | 19p13.3 | Q96G46 | details |
| tRNA-dihydrouridine synthase 4-like | DUS4L | 7q22-q31 | O95620 | details |
| FAD-dependent oxidoreductase domain-containing protein 1 | FOXRED1 | 11q24.2 | Q96CU9 | details |
| FAD-dependent oxidoreductase domain-containing protein 2 | FOXRED2 | 22q12.3 | Q8IWF2 | details |
| Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A | KDM1A | 1p36.12 | O60341 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL1 | MICAL1 | 6q21 | Q8TDZ2 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL2 | MICAL2 | 11p15.3 | O94851 | details |
| Protein-methionine sulfoxide oxidase MICAL3 | MICAL3 | 22q11.21 | Q7RTP6 | details |
| NADPH-dependent diflavin oxidoreductase 1 | NDOR1 | 9q34.3 | Q9UHB4 | details |
| NADPH oxidase 1 | NOX1 | | Q9Y5S8 | details |
| NADPH oxidase 4 | NOX4 | 11q14.2-q21 | Q9NPH5 | details |
| L-amino-acid oxidase | IL4I1 | 19q13.3-q13.4 | Q96RQ9 | details |
| Oxidoreductase NAD-binding domain-containing protein 1 | OXNAD1 | 3p25-p24 | Q96HP4 | details |
| Prenylcysteine oxidase 1 | PCYOX1 | 2p13.3 | Q9UHG3 | details |
| Prenylcysteine oxidase-like | PCYOX1L | 5q32 | Q8NBM8 | details |
| [Pyruvate dehydrogenase [acetyl-transferring]]-phosphatase 2, mitochondrial | PDP2 | 16q22.1 | Q9P2J9 | details |
| Pyridine nucleotide-disulfide oxidoreductase domain-containing protein 1 | PYROXD1 | 12p12.1 | Q8WU10 | details |
| Sulfhydryl oxidase 1 | QSOX1 | 1q24 | O00391 | details |
| Sulfhydryl oxidase 2 | QSOX2 | 9q34.3 | Q6ZRP7 | details |
| Renalase | RNLS | 10q23.31 | Q5VYX0 | details |
| All-trans-retinol 13,14-reductase | RETSAT | 2p11.2 | Q6NUM9 | details |
| Sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase, mitochondrial | SQRDL | 15q15 | Q9Y6N5 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP1 | STEAP1 | 7q21 | Q9UHE8 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP2 | STEAP2 | 7q21 | Q8NFT2 | details |
| Metalloreductase STEAP4 | STEAP4 | 7q21.12 | Q687X5 | details |
| NADH dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) 1 beta subcomplex, 2, 8kDa | NDUFB2 | 7q34 | A4D1T5 | details |