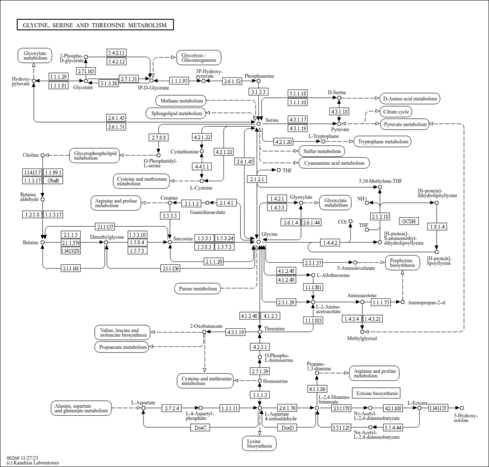
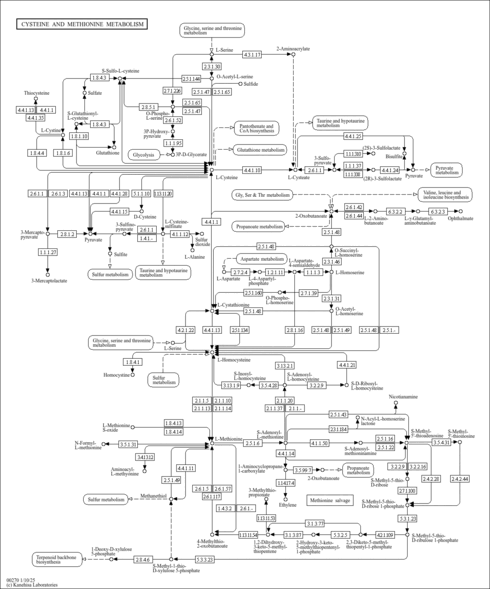
| Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase | PEMT | 17p11.2 | Q9UBM1 | details |
| Acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase | ASMT | Xp22.3 or Yp11.3 | P46597 | details |
| Methionine synthase | MTR | 1q43 | Q99707 | details |
| Catechol O-methyltransferase | COMT | 22q11.21 | P21964 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase, H3 lysine-79 specific | DOT1L | 19p13.3 | Q8TEK3 | details |
| Glycine N-methyltransferase | GNMT | 6p12 | Q14749 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD7 | SETD7 | 4q28 | Q8WTS6 | details |
| S-adenosylmethionine synthase isoform type-2 | MAT2A | 2p11.2 | P31153 | details |
| Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase | PNMT | 17q | P11086 | details |
| Diphthine synthase | DPH5 | 1p21.2 | Q9H2P9 | details |
| Arsenite methyltransferase | AS3MT | 10q24.32 | Q9HBK9 | details |
| Mitochondrial tRNA-specific 2-thiouridylase 1 | TRMU | 22q13 | O75648 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase, H3 lysine-36 and H4 lysine-20 specific | NSD1 | 5q35 | Q96L73 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETDB1 | SETDB1 | 1q21 | Q15047 | details |
| Protein-L-isoaspartate(D-aspartate) O-methyltransferase | PCMT1 | 6q24-q25 | P22061 | details |
| Protein-S-isoprenylcysteine O-methyltransferase | ICMT | 1p36.21 | O60725 | details |
| Indolethylamine N-methyltransferase | INMT | 7p14.3 | O95050 | details |
| DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3A | DNMT3A | 2p23 | Q9Y6K1 | details |
| Hexaprenyldihydroxybenzoate methyltransferase, mitochondrial | COQ3 | 6q16.2 | Q9NZJ6 | details |
| S-adenosylmethionine synthase isoform type-1 | MAT1A | 10q22 | Q00266 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT2 | EHMT2 | 6p21.31 | Q96KQ7 | details |
| S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase proenzyme | AMD1 | 6q21 | P17707 | details |
| Methionine synthase reductase | MTRR | 5p15.31 | Q9UBK8 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H1 | SUV39H1 | Xp11.23 | O43463 | details |
| Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase | NNMT | 11q23.1 | P40261 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV39H2 | SUV39H2 | 10p13 | Q9H5I1 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT1 | EHMT1 | 9q34.3 | Q9H9B1 | details |
| Guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase | GAMT | 19p13.3 | Q14353 | details |
| Histamine N-methyltransferase | HNMT | 2q22.1 | P50135 | details |
| Thiopurine S-methyltransferase | TPMT | 6p22.3 | P51580 | details |
| N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit | METTL3 | 14q11.1 | Q86U44 | details |
| Putative adenosylhomocysteinase 3 | AHCYL2 | 7q32.1 | Q96HN2 | details |
| Adenosylhomocysteinase | AHCY | 20q11.22 | P23526 | details |
| Putative adenosylhomocysteinase 2 | AHCYL1 | 1p13.2 | O43865 | details |
| Cystathionine beta-synthase | CBS | 21q22.3 | P35520 | details |
| Lipoyl synthase, mitochondrial | LIAS | 4p14 | O43766 | details |
| Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 5 | PRMT5 | 14q11.2 | O14744 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1A | SETD1A | 16p11.2 | O15047 | details |
| rRNA 2'-O-methyltransferase fibrillarin | FBL | 19q13.1 | P22087 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL | MLL | 11q23 | Q03164 | details |
| DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3B | DNMT3B | 20q11.2 | Q9UBC3 | details |
| tRNA (cytosine(38)-C(5))-methyltransferase | TRDMT1 | 10p15.1 | O14717 | details |
| N-lysine methyltransferase SETD8 | SETD8 | 12q24.31 | Q9NQR1 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL3 | MLL3 | 7q36.1 | Q8NEZ4 | details |
| Methionine adenosyltransferase 2 subunit beta | MAT2B | | Q9NZL9 | details |
| DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 | DNMT1 | 19p13.2 | P26358 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETDB2 | SETDB2 | 13q14 | Q96T68 | details |
| S-adenosylmethionine mitochondrial carrier protein | SLC25A26 | 3p14.1 | Q70HW3 | details |
| tRNA (cytosine(34)-C(5))-methyltransferase | NSUN2 | 5p15.31 | Q08J23 | details |
| 2-methoxy-6-polyprenyl-1,4-benzoquinol methylase, mitochondrial | COQ5 | 12q24.31 | Q5HYK3 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase ASH1L | ASH1L | 1q22 | Q9NR48 | details |
| N-acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase-like protein | ASMTL | | O95671 | details |
| Histone-arginine methyltransferase CARM1 | CARM1 | 19p13.2 | Q86X55 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH2 | EZH2 | 7q35-q36 | Q15910 | details |
| rRNA/tRNA 2'-O-methyltransferase fibrillarin-like protein 1 | FBLL1 | 5q34 | A6NHQ2 | details |
| Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 2 | LCMT2 | 15q15.3 | O60294 | details |
| mRNA cap guanine-N7 methyltransferase | RNMT | 18p11.21 | O43148 | details |
| Probable S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyltransferase METT5D1 | METT5D1 | 11p14.1 | A6NJ78 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL2 | MLL2 | 12q13.12 | O14686 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL4 | WBP7 | 19q13.1 | Q9UMN6 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase MLL5 | MLL5 | 7q22.1 | Q8IZD2 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase NSD2 | WHSC1 | 4p16.3 | O96028 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase NSD3 | WHSC1L1 | 8p11.2 | Q9BZ95 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN5C | NSUN5P2 | 7q11.23 | Q63ZY6 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN3 | NSUN3 | 3q11.1 | Q9H649 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN4 | NSUN4 | 1p34 | Q96CB9 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN5 | NSUN5 | 7q11.23 | Q96P11 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN6 | NSUN6 | 10p12.31 | Q8TEA1 | details |
| Putative methyltransferase NSUN7 | NSUN7 | 4p14 | Q8NE18 | details |
| Putative tRNA (cytidine(32)/guanosine(34)-2'-O)-methyltransferase | FTSJ1 | Xp11.23 | Q9UET6 | details |
| Putative ribosomal RNA methyltransferase 2 | FTSJ2 | 7p22 | Q9UI43 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD1B | SETD1B | 12q24.31 | Q9UPS6 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD2 | SETD2 | 3p21.31 | Q9BYW2 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETMAR | SETMAR | 3p26.1 | Q53H47 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SMYD3 | SMYD3 | 1q44 | Q9H7B4 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV420H1 | SUV420H1 | 11q13.2 | Q4FZB7 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SUV420H2 | SUV420H2 | 19q13.42 | Q86Y97 | details |
| Probable methyltransferase TARBP1 | TARBP1 | 1q42.3 | Q13395 | details |
| Dimethyladenosine transferase 1, mitochondrial | TFB1M | 6q25.1-q25.3 | Q8WVM0 | details |
| Dimethyladenosine transferase 2, mitochondrial | TFB2M | 1q44 | Q9H5Q4 | details |
| tRNA guanosine-2'-O-methyltransferase TRM11 homolog | TRMT11 | 6q11.1-q22.33 | Q7Z4G4 | details |
| tRNA (guanine(26)-N(2))-dimethyltransferase | TRMT1 | 19p13.2 | Q9NXH9 | details |
| tRNA (adenine(58)-N(1))-methyltransferase catalytic subunit TRMT61A | TRMT61A | 14q32 | Q96FX7 | details |
| tRNA (guanine-N(7)-)-methyltransferase | METTL1 | 12q13 | Q9UBP6 | details |
| tRNA (adenine(58)-N(1))-methyltransferase, mitochondrial | TRMT61B | 2p23.2 | Q9BVS5 | details |
| tRNA (guanine(37)-N1)-methyltransferase | TRMT5 | 14q23.1 | Q32P41 | details |
| Probable S-adenosyl-L-methionine-dependent methyltransferase METT5D2 | METT5D2 | 3q25.31 | P0C7V9 | details |
| Transmembrane O-methyltransferase | LRTOMT | 11q13.4 | Q8WZ04 | details |
| DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 3-like | DNMT3L | | Q9UJW3 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EZH1 | EZH1 | 17q21.1-q21.3 | Q92800 | details |
| Leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 | LCMT1 | 16p12.1 | Q9UIC8 | details |
| tRNA (uracil(54)-C(5))-methyltransferase homolog | TRMT2B | Xq22.1 | Q96GJ1 | details |
| Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 | PRMT1 | 19q13.3 | Q99873 | details |
| Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 2 | PRMT2 | 21q22.3 | P55345 | details |
| Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 6 | PRMT6 | 1p13.3 | Q96LA8 | details |
| Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 7 | PRMT7 | 16q22.1 | Q9NVM4 | details |
| Calmodulin-lysine N-methyltransferase | CAMKMT | 2p21 | Q7Z624 | details |
| Probable dimethyladenosine transferase | DIMT1 | 5q12.1 | Q9UNQ2 | details |
| HemK methyltransferase family member 1 | HEMK1 | | Q9Y5R4 | details |
| Small RNA 2'-O-methyltransferase | HENMT1 | 1p13.3 | Q5T8I9 | details |
| Methyltransferase-like protein 2B | METTL2B | | Q6P1Q9 | details |
| Methyltransferase-like protein 6 | METTL6 | | Q8TCB7 | details |
| Cap-specific mRNA (nucleoside-2'-O-)-methyltransferase 1 | FTSJD2 | 6p21.2 | Q8N1G2 | details |
| Ribosomal RNA small subunit methyltransferase NEP1 | EMG1 | 12p13.3 | Q92979 | details |
| N-terminal Xaa-Pro-Lys N-methyltransferase 1 | NTMT1 | 9q34.11 | Q9BV86 | details |
| Alpha N-terminal protein methyltransferase 1B | METTL11B | 1q24.2 | Q5VVY1 | details |
| Putative histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM6 | PRDM6 | 5q23.2 | Q9NQX0 | details |
| Probable histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM7 | PRDM7 | 16q24.3 | Q9NQW5 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase PRDM9 | PRDM9 | 5p14 | Q9NQV7 | details |
| Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase setd3 | SETD3 | 14q32.2 | Q86TU7 | details |
| N-lysine methyltransferase SMYD2 | SMYD2 | 1q32.3 | Q9NRG4 | details |
| Trimethylguanosine synthase | TGS1 | 8q11 | Q96RS0 | details |
| Probable tRNA (uracil-O(2)-)-methyltransferase | TRMT44 | 4p16.1 | Q8IYL2 | details |
| Uncharacterized methyltransferase WBSCR22 | WBSCR22 | | O43709 | details |