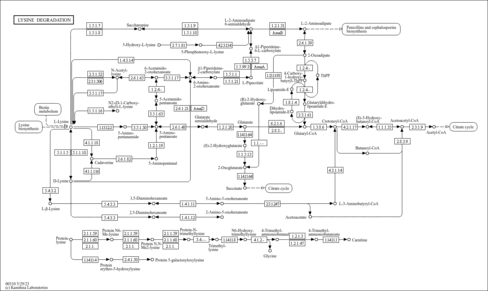
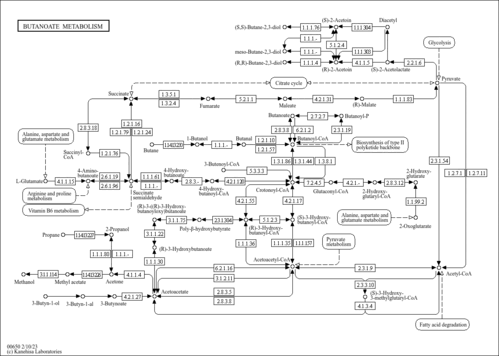
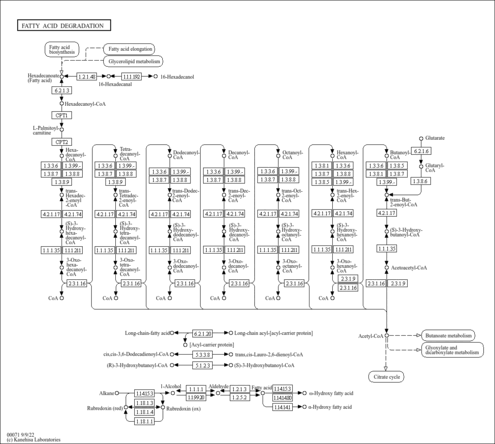
| 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, mitochondrial | ACAA2 | 18q21.1 | P42765 | details |
| 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, peroxisomal | ACAA1 | 3p22.2 | P09110 | details |
| Trifunctional enzyme subunit beta, mitochondrial | HADHB | 2p23 | P55084 | details |
| Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial | ALDH6A1 | 14q24.3 | Q02252 | details |
| Long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADL | 2q34 | P28330 | details |
| Short-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADS | 12q24.31 | P16219 | details |
| Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADM | 1p31 | P11310 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1 | ACOX1 | 17q25.1 | Q15067 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 2 | ACOX2 | 3p14.3 | Q99424 | details |
| Isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | IVD | 15q14-q15 | P26440 | details |
| Peroxisomal acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 3 | ACOX3 | 4p15.3 | O15254 | details |
| Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | GCDH | 19p13.2 | Q92947 | details |
| Hepatic triacylglycerol lipase | LIPC | 15q21-q23 | P11150 | details |
| Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 | DGAT1 | 8q24.3 | O75907 | details |
| 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit beta, mitochondrial | BCKDHB | 6q14.1 | P21953 | details |
| 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase subunit alpha, mitochondrial | BCKDHA | 19q13.1-q13.2 | P12694 | details |
| Acyl-CoA desaturase | SCD | 10q24.31 | O00767 | details |
| Enoyl-CoA hydratase, mitochondrial | ECHS1 | 10q26.2-q26.3 | P30084 | details |
| Sterol O-acyltransferase 2 | SOAT2 | 12q13.13 | O75908 | details |
| Sterol O-acyltransferase 1 | SOAT1 | 1q25 | P35610 | details |
| Bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase | BAAT | 9q22.3 | Q14032 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4 | ACSL4 | Xq22.3-q23 | O60488 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 1 | ACSL1 | 4q35 | P33121 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 6 | ACSL6 | 5q31 | Q9UKU0 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 5 | ACSL5 | 10q25.1-q25.2 | Q9ULC5 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 3 | ACSL3 | 2q34-q35 | O95573 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial | GPAM | 10q25.2 | Q9HCL2 | details |
| Trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase, mitochondrial | MECR | 1p35.3 | Q9BV79 | details |
| Peroxisomal trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase | PECR | 2q35 | Q9BY49 | details |
| Cytosolic acyl coenzyme A thioester hydrolase | ACOT7 | 1p36 | O00154 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 2, mitochondrial | ACOT2 | 14q24.3 | P49753 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 4 | ACOT4 | 14q24.3 | Q8N9L9 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 8 | ACOT8 | 20q13.12 | O14734 | details |
| Dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase | GNPAT | 1q42 | O15228 | details |
| 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase gamma | AGPAT3 | 21q22.3 | Q9NRZ7 | details |
| 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase beta | AGPAT2 | 9q34.3 | O15120 | details |
| 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase alpha | AGPAT1 | 6p21.3 | Q99943 | details |
| Short/branched chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADSB | 10q26.13 | P45954 | details |
| Very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase | SLC27A2 | 15q21.2 | O14975 | details |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | PPARG | 3p25 | P37231 | details |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha | PPARA | 22q12-q13.1|22q13.31 | Q07869 | details |
| Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta | PPARD | 6p21.2 | Q03181 | details |
| Acyl-CoA-binding protein | DBI | 2q12-q21 | P07108 | details |
| Fatty acid-binding protein, heart | FABP3 | 1p33-p32 | P05413 | details |
| 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase epsilon | AGPAT5 | 8p23.1 | Q9NUQ2 | details |
| Bile acyl-CoA synthetase | SLC27A5 | 19q13.43 | Q9Y2P5 | details |
| Lipoamide acyltransferase component of branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex, mitochondrial | DBT | 1p31 | P11182 | details |
| 2-acylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 | MOGAT2 | 11q13.5 | Q3SYC2 | details |
| Long-chain fatty acid transport protein 3 | SLC27A3 | 1q21.3 | Q5K4L6 | details |
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 10 | ACAD10 | 12q24.12 | Q6JQN1 | details |
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 11 | ACAD11 | 3q22.1 | Q709F0 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 4 | AGPAT6 | 8p11.21 | Q86UL3 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM1, mitochondrial | ACSM1 | 16p12.3 | Q08AH1 | details |
| Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2 | DGAT2 | 11q13.5 | Q96PD7 | details |
| 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase delta | AGPAT4 | 6q26 | Q9NRZ5 | details |
| 2-acylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 | MOGAT1 | 2q36.1 | Q96PD6 | details |
| Isobutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACAD8 | 11q25 | Q9UKU7 | details |
| Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 9, mitochondrial | ACAD9 | 3q21.3 | Q9H845 | details |
| Long-chain fatty acid transport protein 4 | SLC27A4 | 9q34.11 | Q6P1M0 | details |
| Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 1 | FAR1 | 11p15.2 | Q8WVX9 | details |
| Fatty acyl-CoA reductase 2 | FAR2 | 12p11.22 | Q96K12 | details |
| Acyl-CoA wax alcohol acyltransferase 1 | AWAT1 | Xq13.1 | Q58HT5 | details |
| Acyl-CoA wax alcohol acyltransferase 2 | AWAT2 | Xq13.1 | Q6E213 | details |
| Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2-like protein 6 | DGAT2L6 | | Q6ZPD8 | details |
| Putative diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2-like protein 7 | DGAT2L7 | 7q22.1 | Q6IED9 | details |
| 2-acylglycerol O-acyltransferase 3 | MOGAT3 | 7q22.1 | Q86VF5 | details |
| Lysophospholipid acyltransferase 5 | LPCAT3 | 12p13 | Q6P1A2 | details |
| Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 | LPCAT1 | 5p15.33 | Q8NF37 | details |
| Lysocardiolipin acyltransferase 1 | LCLAT1 | 2p23.1 | Q6UWP7 | details |
| Lysophospholipid acyltransferase LPCAT4 | LPCAT4 | 15q14 | Q643R3 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 3 | AGPAT9 | 4q21.23 | Q53EU6 | details |
| Glycine N-acyltransferase | GLYAT | 11q12.1 | Q6IB77 | details |
| Glycine N-acyltransferase-like protein 1 | GLYATL1 | 11q12.1 | Q969I3 | details |
| Glycine N-acyltransferase-like protein 2 | GLYATL2 | 11q12.1 | Q8WU03 | details |
| Enoyl-CoA delta isomerase 2, mitochondrial | ECI2 | 6p24.3 | O75521 | details |
| Acyl-CoA synthetase family member 4 | AASDH | 4q12 | Q4L235 | details |
| Very long-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ACADVL | 17p13.1 | P49748 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A oxidase-like protein | ACOXL | 2q13 | Q9NUZ1 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM6, mitochondrial | ACSM6 | 10q23.33 | Q6P461 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM2A, mitochondrial | ACSM2A | 16p12.3 | Q08AH3 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM2B, mitochondrial | ACSM2B | 16p12.3 | Q68CK6 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM3, mitochondrial | ACSM3 | 16p13.11 | Q53FZ2 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM5, mitochondrial | ACSM5 | 16p12.3 | Q6NUN0 | details |
| Peroxisomal coenzyme A diphosphatase NUDT7 | NUDT7 | 16q23.1 | P0C024 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase ACSM4, mitochondrial | ACSM4 | 12p13.31 | P0C7M7 | details |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 2, mitochondrial | GPAT2 | 2q11.1 | Q6NUI2 | details |
| Peroxisomal D3,D2-enoyl-CoA isomerase isoform 1 variant | | | Q53GC8 | details |
| Nef-associated protein 1 | C9orf156 | 9q22.33 | Q9BU70 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 9, mitochondrial | ACOT9 | | Q9Y305 | details |
| Acyl-CoA synthetase family member 3, mitochondrial | ACSF3 | 16q24.3 | Q4G176 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 1 | ACOT1 | 14q24.3 | Q86TX2 | details |
| Cytosolic acyl coenzyme A thioester hydrolase-like | ACOT7L | | Q6ZUV0 | details |
| Acyl-CoA synthetase family member 2, mitochondrial | ACSF2 | 17q21.33 | Q96CM8 | details |
| Acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 11 | ACOT11 | 1p32.3 | Q8WXI4 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase ACSBG2 | ACSBG2 | 19p13.3 | Q5FVE4 | details |
| Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase ACSBG1 | ACSBG1 | 15q23-q24 | Q96GR2 | details |