| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-04-17 19:14:16 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-11-18 16:39:26 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB005149 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate |
|---|
| Description | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, also known as 3-phosphoadenosine 5-phosphate or 3'-phosphoadenylate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphates. These are purine ribobucleotides with one phosphate group attached to 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the ribose moiety. Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate is a strong basic compound (based on its pKa). Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Outside of the human body, Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as scarlet beans, tronchuda cabbages, horseradish tree, shallots, and lindens. This could make adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. An adenosine bisphosphate having two monophosphate groups at the 3'- and 5'-positions. Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate is expected to be in Cannabis as all living plants are known to produce and metabolize it. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3'-Phosphoadenylate | ChEBI | | Adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate | ChEBI | | PAP | ChEBI | | Phosphoadenosine phosphate | ChEBI | | 3'-Phosphoadenylic acid | Generator | | Adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphoric acid | Generator | | Phosphoadenosine phosphoric acid | Generator | | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphoric acid | Generator | | 3'-Phosphoryl-AMP | HMDB | | 3,5-ADP | HMDB | | 3,5-Diphosphoadenosine | HMDB | | 3-Phosphoadenosine 5-phosphate | HMDB | | 5-(Dihydrogen phosphate) 3-adenylate | HMDB | | 5-(Dihydrogen phosphate)3'-adenylic acid | HMDB | | Adenosine 3,5-bis | HMDB | | Adenosine 3,5-bisphosphate | HMDB | | Adenosine 3'-phosphate-5'-phosphate, disodium salt | HMDB | | 3'-Phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate | HMDB | | Adenosine 3'-phosphate-5'-phosphate, monosodium salt | HMDB | | 3',5'-ADP | HMDB | | Adenosine 3'-phosphate-5'-phosphate | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C10H15N5O10P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 427.2 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 427.0294 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | {[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy}phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | adenosine 3',5'-bisphosphate |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1053-73-2 |
|---|
| SMILES | NC1=C2N=CN([C@@H]3O[C@H](COP(O)(O)=O)[C@@H](OP(O)(O)=O)[C@H]3O)C2=NC=N1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H15N5O10P2/c11-8-5-9(13-2-12-8)15(3-14-5)10-6(16)7(25-27(20,21)22)4(24-10)1-23-26(17,18)19/h2-4,6-7,10,16H,1H2,(H2,11,12,13)(H2,17,18,19)(H2,20,21,22)/t4-,6-,7-,10-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WHTCPDAXWFLDIH-KQYNXXCUSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphates. These are purine ribobucleotides with one phosphate group attached to 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the ribose moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
|---|
| Class | Purine nucleotides |
|---|
| Sub Class | Purine ribonucleotides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Purine ribonucleoside 3',5'-bisphosphate
- Purine ribonucleoside monophosphate
- Pentose phosphate
- Ribonucleoside 3'-phosphate
- Pentose-5-phosphate
- Glycosyl compound
- N-glycosyl compound
- 6-aminopurine
- Pentose monosaccharide
- Monosaccharide phosphate
- Imidazopyrimidine
- Purine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- N-substituted imidazole
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Monosaccharide
- Imidolactam
- Pyrimidine
- Alkyl phosphate
- Imidazole
- Azole
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Secondary alcohol
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 614.5 mg/mL | Not Available | | logP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-9332100000-c2cf1343058e5c460684 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, 1 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-9141400000-8e8cf251eecd6d39cf02 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TMS_1_4, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TBDMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TBDMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TBDMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate, TBDMS_1_4, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 10V, positive | splash10-000i-0913100000-4559e980fc823f06cda1 | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 20V, positive | splash10-000i-0910000000-164b37f4075a5627b64d | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 40V, positive | splash10-000i-1900000000-0f28c9a19c771609202d | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 35V, Negative | splash10-003r-3900000000-fc11f9ff14bc678ffb89 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-057i-2913300000-fdb650a7ed3a1d7dc119 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0059-9700000000-e0ed082bd1249fa162f6 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000i-1900000000-a2612ac21c9094d3d4b1 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 35V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-a48b75d77591f32a31a6 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0910000000-164b37f4075a5627b64d | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0913100000-5a86462d5152e2e074f0 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0101900000-c682799b7471e544d5a7 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0902300000-77268ef9fe8672f81e9f | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-6986eb10675f363acf42 | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000i-1900000000-493254661a51349997bd | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-7801900000-b4b0af4deca129a6a12c | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0059-9800000000-4a1ffcf05d9938fe121e | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-9200000000-fb4a5bf16d0e5bcaa1e0 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-63709bad7395f9f33acc | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-001i-0900100000-1be0541745ea8310e717 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-003r-4901000000-46fabb89b3c8f5f65bc8 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-0000900000-e292158e80c5681369df | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0019-0923500000-c2fa14d2158399b30f0c | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-001r-1779000000-aed0b018efcf2528cabd | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Sulfate/Sulfite Metabolism |    | 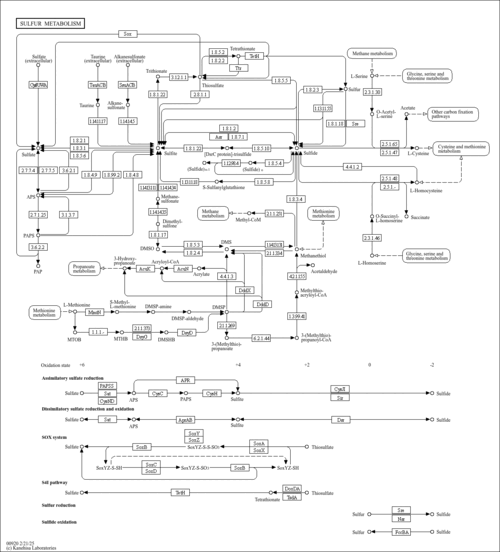 | | Sulfite oxidase deficiency |    | Not Available | | Sphingolipid Metabolism |    |  | | Gaucher Disease |    | Not Available | | Globoid Cell Leukodystrophy |    | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 1 | ENPP1 | 6q22-q23 | P22413 | details | | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3 | ENPP3 | 6q22 | O14638 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11 | CHST11 | 12q | Q9NPF2 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 | CHST3 | 10q22.1 | Q7LGC8 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 13 | CHST13 | 3q21.3 | Q8NET6 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 12 | CHST12 | 7p22 | Q9NRB3 | details | | Galactosylceramide sulfotransferase | GAL3ST1 | 22q12.2 | Q99999 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 3B1 | HS3ST3B1 | 17p12 | Q9Y662 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 3A1 | HS3ST3A1 | 17p12 | Q9Y663 | details | | Sulfotransferase 1A1 | SULT1A1 | 16p12.1 | P50225 | details | | 3'(2'),5'-bisphosphate nucleotidase 1 | BPNT1 | 1q41 | O95861 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 1 | HS3ST1 | 4p16 | O14792 | details | | Estrogen sulfotransferase | SULT1E1 | 4q13.1 | P49888 | details | | Bile salt sulfotransferase | SULT2A1 | 19q13.3 | Q06520 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 1 | CHST1 | 11p11.2 | O43916 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 4 | HS3ST4 | 16p11.2 | Q9Y661 | details | | Sulfotransferase 1A2 | SULT1A2 | 16p12.1 | P50226 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 5 | HS3ST5 | 6q21 | Q8IZT8 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 2 | HS3ST2 | 16p12 | Q9Y278 | details | | Protein-tyrosine sulfotransferase 2 | TPST2 | 22q12.1 | O60704 | details | | Sulfotransferase family cytosolic 2B member 1 | SULT2B1 | 19q13.3 | O00204 | details | | Sulfotransferase 1A3/1A4 | SULT1A3 | 16p11.2 | P50224 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 7 | CHST7 | Xp11.23 | Q9NS84 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14 | CHST14 | 15q15.1 | Q8NCH0 | details | | Heparan-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase 1 | HS6ST1 | 2q21 | O60243 | details | | Heparan-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase 2 | HS6ST2 | Xq26.2 | Q96MM7 | details | | Heparan-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase 3 | HS6ST3 | 13q32.1 | Q8IZP7 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 15 | CHST15 | 10q26 | Q7LFX5 | details | | Inositol monophosphatase 3 | IMPAD1 | 8q12.1 | Q9NX62 | details | | Tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase 1 | TPST1 | 7q11.21 | A4D2M0 | details | | L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase-phosphopantetheinyl transferase | AASDHPPT | 11q22 | Q9NRN7 | details | | Heparan sulfate glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 6 | HS3ST6 | | Q96QI5 | details | | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 | NDST1 | 5q33.1 | P52848 | details | | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 2 | NDST2 | 10q22 | P52849 | details | | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 3 | NDST3 | 4q26 | O95803 | details | | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 4 | NDST4 | 4q26 | Q9H3R1 | details | | Sulfotransferase 1C3 | SULT1C3 | 2q12.3 | Q6IMI6 | details | | Sulfotransferase 6B1 | SULT6B1 | | Q6IMI4 | details | | Protein-tyrosine sulfotransferase 1 | TPST1 | 7q11.21 | O60507 | details |
|
|---|
| Transporters | Not Available |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 1 | ENPP1 | 6q22-q23 | P22413 | details | | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3 | ENPP3 | 6q22 | O14638 | details | | Inositol monophosphatase 3 | IMPAD1 | 8q12.1 | Q9NX62 | details | | L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase-phosphopantetheinyl transferase | AASDHPPT | 11q22 | Q9NRN7 | details |
|
|---|
| Receptors | |
| Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 1 | ENPP1 | 6q22-q23 | P22413 | details | | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 3 | ENPP3 | 6q22 | O14638 | details | | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11 | CHST11 | 12q | Q9NPF2 | details | | Bifunctional heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 | NDST1 | 5q33.1 | P52848 | details |
|
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000061 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01812 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB030650 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00019352 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 140102 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00054 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | 3-5-ADP |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33684 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 159296 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17985 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|

