| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-03-19 00:26:12 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:07:17 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB000237 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | beta-D-Glucose |
|---|
| Description | β-D-Glucopyranose is one of the four cyclic isomers of D-glucose. Glucose (CAS: 50-99-7) is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group and is therefore referred to as an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) and ring (cyclic) form, the latter being the result of an intramolecular reaction between the aldehyde C atom and the C-5 hydroxyl group to form an intramolecular hemiacetal. In aqueous solution, both forms are in equilibrium and at pH 7 the cyclic one is predominant. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates and it is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, as such it is also found in Cannabis sativa (PMID: 6991645 ). In plants and algae, it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, which is the most abundant carbohydrate polymer found in nature. Glucose is a primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. In animals, glucose arises from the breakdown of glycogen in a process known as glycogenolysis. Glucose is synthesized in the liver and kidneys from non-carbohydrate intermediates, such as pyruvate and glycerol, by a process known as gluconeogenesis. D-Glucose is found to be associated with 3-methyl-crotonyl-glycinuria, growth hormone deficiency, and primary hypomagnesemia, which are inborn errors of metabolism. Glucose is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2122h-1b_1-5]/1/ | ChEBI | | beta-D-Glucopyranose | Kegg | | b-D-Glucopyranose | Generator | | Glucose | ChEMBL, HMDB | | b-D-Glucose | Generator | | β-D-glucose | Generator | | b-Dextrose | HMDB | | b-Glucose | HMDB | | beta-Dextrose | HMDB | | beta-Glucose | HMDB | | D Glucose | MeSH, HMDB | | Glucose, (beta-D)-isomer | MeSH, HMDB | | Dextrose | MeSH, HMDB | | Glucose, (DL)-isomer | MeSH, HMDB | | D-Glucose | MeSH, HMDB | | D-Glucopyranose | HMDB | | D-Glucopyranoside | HMDB | | beta-D-Glucopyranoside | HMDB | | beta-D-Glucose | HMDB | | β-D-Glucopyranoside | HMDB | | β-D-Glucose | HMDB | | β-Dextrose | HMDB | | β-Glucose | HMDB | | D-GLC | HMDB | | D-GLCP | HMDB | | GLC-OH | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H12O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 180.16 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 180.0634 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | glucoside |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 108942-17-2 |
|---|
| SMILES | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hexoses. These are monosaccharides in which the sugar unit is a is a six-carbon containing moeity. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Hexoses |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Hexose monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Secondary alcohol
- Hemiacetal
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Primary alcohol
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Physiological effect | Health effect: |
|---|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: Biological role: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 146 - 150 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 1200 mg/mL | Not Available | | logP | -3.24 | SANGSTER (1994) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| EI-MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-03kc-9000000000-a60df7b043f8947d6909 | 2015-03-01 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9721000000-6ca4df9ac892160d11c5 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9621000000-fff85ff382393ec04a54 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9721000000-6ca4df9ac892160d11c5 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9621000000-fff85ff382393ec04a54 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0np0-9700000000-e8d638dc817e46b97d7b | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, 5 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004i-6122690000-eaf6f7adf34ccd0c667b | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_1_4, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_1_5, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_4, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_5, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_6, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_7, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_8, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_9, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_2_10, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_3_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | beta-D-Glucose, TMS_3_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-0002-9300000000-839f41cf94a071fcdb37 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-0002-9000000000-807f75d14f3d0b66f5bd | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, N/A (Annotated) | splash10-000t-9000000000-b89668f86992a8363664 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-7900000000-9a673c2e4b82ca397421 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4r-9100000000-b70415588e768ddce5ef | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-73dc84dd88d8ae69fe02 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-ba39d4ed9431a1d01eab | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-a61efd1469735758b317 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-000i-7900000000-9a673c2e4b82ca397421 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4r-9100000000-9c25b149885d8a48aab5 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-76d92ea96364c24ecfb0 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-ba39d4ed9431a1d01eab | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-a61efd1469735758b317 | 2020-03-26 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 1V, positive | splash10-03di-0900000000-c44bda60a6fcba163df3 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 2V, positive | splash10-03di-0900000000-2d4fcc06b5f1a548e0ac | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 3V, positive | splash10-03dj-1900000000-d66ef20973a9aed890d5 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 4V, positive | splash10-01ot-2900000000-f15e86af30f3065466a8 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 5V, positive | splash10-000b-4900000000-2a9008fcc11325c7a3fe | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 6V, positive | splash10-000b-7900000000-afd4ac776eb4bedb6bff | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 7V, positive | splash10-000j-9700000000-394bb6f6163ff53c203a | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 8V, positive | splash10-000i-9400000000-afcfe7141c6578d96206 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 9V, positive | splash10-000i-9300000000-011aa587ff83208ceaa6 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 10V, positive | splash10-000i-9200000000-8d13450ee922cef5d173 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 11V, positive | splash10-000i-9200000000-ba587aac166359ffc7d5 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 12V, positive | splash10-000i-9100000000-e62915efe3ed02f208b6 | 2020-07-22 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 125 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Glycolysis |    | 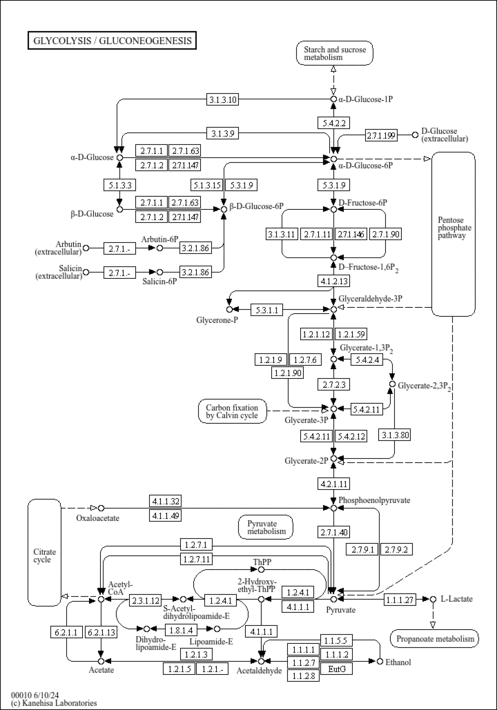 | | Galactose Metabolism |    | 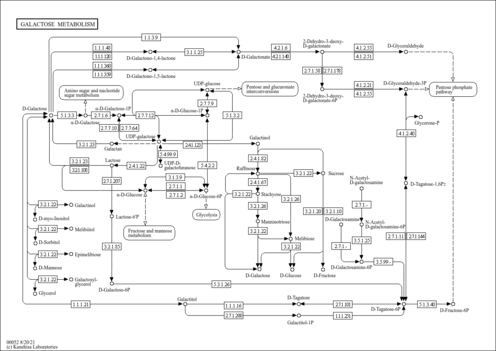 | | Gluconeogenesis |    |  | | Glucose-Alanine Cycle |    | Not Available | | Lactose Synthesis |    | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
|---|
| Transporters | |
| Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 | SLC2A1 | 1p34.2 | P11166 | details |
|
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000122 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB02379 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB011824 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001122 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 58238 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00221 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | GLC |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Glucose |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 64689 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15903 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | - Turner CE, Elsohly MA, Boeren EG: Constituents of Cannabis sativa L. XVII. A review of the natural constituents. J Nat Prod. 1980 Mar-Apr;43(2):169-234. doi: 10.1021/np50008a001. [PubMed:6991645 ]
|
|---|

