| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-04-17 18:43:02 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:11:06 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB004848 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | L-Cysteine |
|---|
| Description | L-Cysteine, also known as C or e 920, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cysteine and derivatives. Cysteine and derivatives are compounds containing cysteine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of cysteine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. L-Cysteine is a drug which is used for the prevention of liver damage and kidney damage associated with overdoses of acetaminophen. L-Cysteine is a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). L-Cysteine exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within humans, L-cysteine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, L-cysteine can be converted into 3-sulfinoalanine; which is mediated by the enzyme cysteine dioxygenase type 1. In addition, L-cysteine can be converted into hydrogen sulfide and pyruvic acid through the action of the enzyme cystathionine gamma-lyase. In humans, L-cysteine is involved in cysteine metabolism. L-Cysteine is a sulfury tasting compound. Outside of the human body, L-Cysteine is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as sunflowers, soy beans, and watermelons and in a lower concentration in common wheats, dates, and beers. L-Cysteine has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as oyster mushrooms, salmonberries, rapes, safflowers, and cupuaçus. This could make L-cysteine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. L-Cysteine is a potentially toxic compound. An optically active form of cysteine having L-configuration. L-Cysteine is expected to be in Cannabis as all living plants are known to produce and metabolize it. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (2R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | ChEBI | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid | ChEBI | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | ChEBI | | C | ChEBI | | Cys | ChEBI | | CYSTEINE | ChEBI | | e 920 | ChEBI | | e-920 | ChEBI | | e920 | ChEBI | | FREE cysteine | ChEBI | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | ChEBI | | L-Cystein | ChEBI | | L-Zystein | ChEBI | | Ecolan | Kegg | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulfanylpropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulphanylpropanoate | Generator | | (2R)-2-Amino-3-sulphanylpropanoic acid | Generator | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | Generator | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionate | Generator | | (+)-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | HMDB | | (R)-(+)-Cysteine | HMDB | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercapto-propanoate | HMDB | | (R)-2-Amino-3-mercapto-propanoic acid | HMDB | | (R)-Cysteine | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionate | HMDB | | 2-Amino-3-mercaptopropionic acid | HMDB | | 3-Mercapto-L-alanine | HMDB | | Acetylcysteine | HMDB | | alpha-Amino-beta-thiolpropionic acid | HMDB | | b-Mercaptoalanine | HMDB | | beta-Mercaptoalanine | HMDB | | Carbocysteine | HMDB | | Cisteina | HMDB | | Cisteinum | HMDB | | Cystein | HMDB | | Cysteinum | HMDB | | Half-cystine | HMDB | | L Cysteine | HMDB | | L-(+)-Cysteine | HMDB | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoate | HMDB | | L-2-Amino-3-mercaptopropanoic acid | HMDB | | Polycysteine | HMDB | | Thioserine | HMDB | | Cysteine hydrochloride | HMDB | | Zinc cysteinate | HMDB | | Half cystine | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C3H7NO2S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 121.16 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 121.0197 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | L-cysteine |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 52-90-4 |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@@H](CS)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C3H7NO2S/c4-2(1-7)3(5)6/h2,7H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | XUJNEKJLAYXESH-REOHCLBHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cysteine and derivatives. Cysteine and derivatives are compounds containing cysteine or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of cysteine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Cysteine and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Cysteine or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid
- L-alpha-amino acid
- Amino acid
- Alkylthiol
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Physiological effect | Health effect: |
|---|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: Biological role: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 220 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 277 mg/mL at 25 °C | BEILSTEIN | | logP | -2.49 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | L-Cysteine, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0950000000-df7e91c95b610ff21c79 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0940000000-aefe34765fb447090a23 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0970000000-10a155c40ea499023052 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0940000000-037a3a34651c3154b3b3 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9850000000-118c43e33861a6baa8d2 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-014j-0690100000-0aeb88fd507505e6b718 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0950000000-df7e91c95b610ff21c79 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0940000000-aefe34765fb447090a23 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0970000000-10a155c40ea499023052 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00kb-0940000000-037a3a34651c3154b3b3 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0uk9-5619100000-8cb2558373966174ced3 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9850000000-118c43e33861a6baa8d2 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0gi0-0960000000-03b2097de6f9637d29cb | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004l-9100000000-4553906a941a5e87ec97 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, 1 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-004i-9200000000-cfaf705cd0452d428454 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, TMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, TMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, TBDMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, TBDMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | L-Cysteine, TBDMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-00b9-9600000000-374c5872d68662832769 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-ddbd3df6b8dbb280ffba | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-320a2c77443b80ebf733 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0089-0900000000-9dcd3d757c5cd11eb18e | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0udi-3900000000-212e081fe83ad70de0ad | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-000i-9000000000-2eb01f41c225f614db24 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-001i-0900000000-a19834eb7cb9f211fdf2 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-00di-0900000000-2458f2587761e779ed93 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-77e590f0ed26f69b31c0 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0udi-3900000000-7b1857997392b006b95f | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Positive | splash10-0a4i-3900000000-bc268c27ed5706a4bbd2 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - CE-ESI-TOF (CE-system connected to 6210 Time-of-Flight MS, Agilent) , Positive | splash10-00di-0900000000-4573390bccc238e3c91b | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0udi-3900000000-212e081fe83ad70de0ad | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0udi-3900000000-7b1857997392b006b95f | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - QqQ 14V, negative | splash10-001i-9000000000-5dc69d3b59bd15290aef | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a6r-9100000000-ed3c9c47ed98679090ab | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 0V, Positive | splash10-00di-2900000000-8bb219d17ccdf7ac0a5d | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 30V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-e623d5a27b5075c82b4d | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-056r-9100000000-4e26cc13af7c878115f7 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00b9-9600000000-4352a7b437c34c04d9f0 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-004i-9200000000-7b4cd034c717561c61dd | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-052f-9000000000-8f351cbca6ffed356a9b | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-6900000000-51ba0df80cc33423420b | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0079-9400000000-4aa2b707c391d5838d29 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001i-9000000000-95c7672c7836c0fc51c9 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 125 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 1H]-TOCSY. Unexported temporarily by An Chi on Oct 15, 2021 until json or nmrML file is generated. 2D NMR Spectrum (experimental) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Glutathione Metabolism |    | 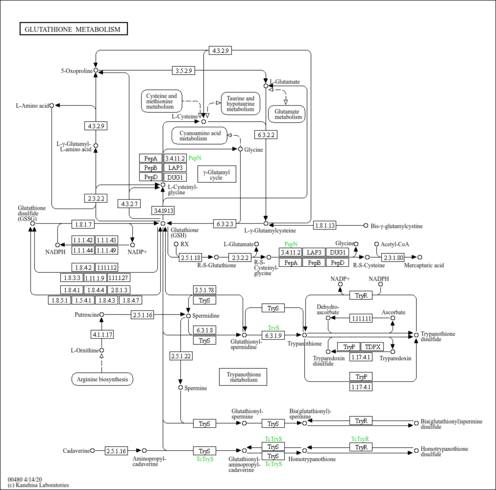 | | Glycine and Serine Metabolism |    | 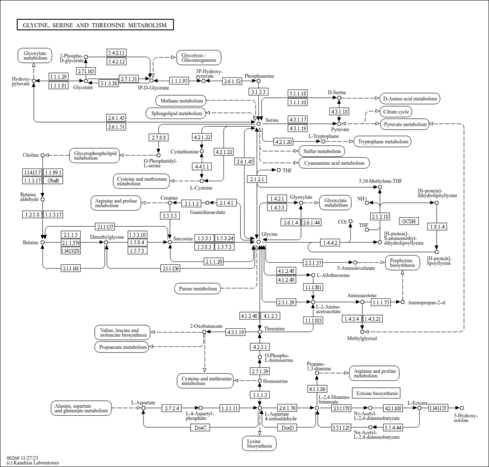 | | Methionine Metabolism |    | 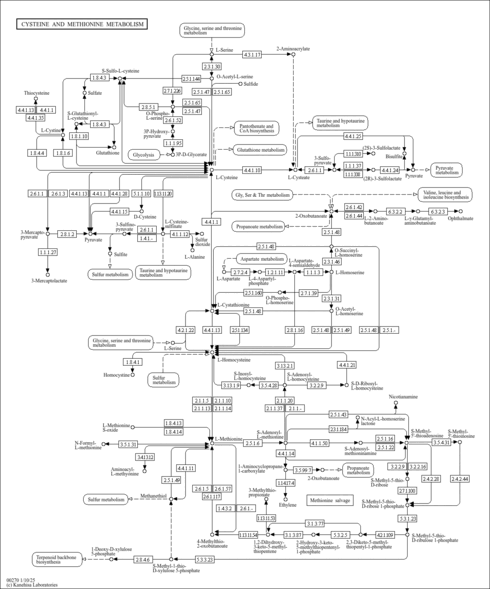 | | Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism |    | 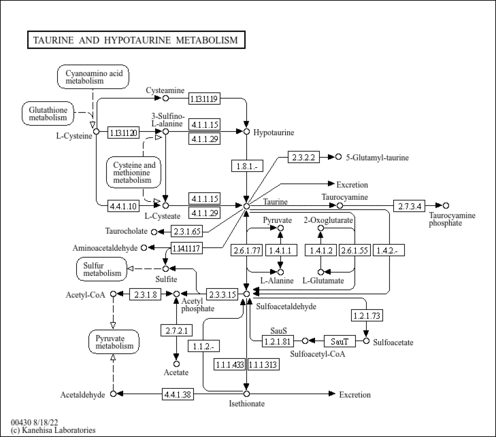 | | Cysteine Metabolism |    |  |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
|---|
| Transporters | |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000574 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00151 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB012678 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001351 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 5653 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00097 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CYS |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 33843 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Cysteine |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 5556 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5862 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 17561 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|



