| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-04-17 19:09:31 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:11:35 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB005102 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydrogen carbonate |
|---|
| Description | Hydrogen carbonate, also known as H2CO3 or [co(OH)2], belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic carbonic acids. Organic carbonic acids are compounds comprising the carbonic acid functional group. Bicarbonate also acts to regulate pH in the small intestine. Hydrogen carbonate is a very weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). A parallel example is sodium bisulfite (NaHSO3). Hydrogen carbonate exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. In humans, hydrogen carbonate is involved in the metabolic disorder called the hartnup disorder pathway. Outside of the human body, Hydrogen carbonate has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as lovages, lima beans, tree ferns, mountain yams, and burbots. This could make hydrogen carbonate a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. As such it is an important sink in the carbon cycle. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid HNO3. Hydrogen carbonate is expected to be in Cannabis as all living plants are known to produce and metabolize it. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| [CO(OH)2] | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen carbonate | ChEBI | | H2CO3 | ChEBI | | Koehlensaeure | ChEBI | | Dihydrogen carbonic acid | Generator | | Hydrogen carbonic acid | Generator | | Carbonate | Generator, HMDB | | Acid OF air | HMDB | | Aerial acid | HMDB | | Bisodium carbonate | HMDB | | Calcined | HMDB | | Carbonic acid sodium salt | HMDB | | Consal | HMDB | | Crystol carbonate | HMDB | | Disodium carbonate | HMDB | | Mild alkali | HMDB | | Na-X | HMDB | | Oxyper | HMDB | | Sal soda | HMDB | | Salt OF soda | HMDB | | Scotch soda | HMDB | | Soda | HMDB | | Soda ash | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate anhydrous | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate hydrated | HMDB | | Sodium carbonate peroxyhydrate | HMDB | | Solvay soda | HMDB | | Trona soda ash | HMDB | | Tronalight light soda ash | HMDB | | Acid, carbonic | MeSH, HMDB | | Carbonic acid | MeSH, HMDB | | Ions, bicarbonate | MeSH | | Carbonate, hydrogen | MeSH | | Carbonates, hydrogen | MeSH | | Bicarbonate ion | MeSH | | Hydrogen carbonates | MeSH | | Bicarbonates | MeSH | | Bicarbonate ions | MeSH | | Carbonic acid ions | MeSH | | Ions, carbonic acid | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | CH2O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 62.02 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 62.0004 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | carbonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | carbonic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 463-79-6 |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/CH2O3/c2-1(3)4/h(H2,2,3,4) |
|---|
| InChI Key | BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic carbonic acids. Organic carbonic acids are compounds comprising the carbonic acid functional group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Organic carbonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Carbonic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: Biological role: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 720 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 12.8 mg/mL (cold water) | MERCK INDEX (1996) | | logP | 0.0 | Wikipedia |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-310dbbc64fba7d9c667e | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, 2 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00du-9300000000-b9ab1da5629a3dfff55f | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, TMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, TBDMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Hydrogen carbonate, TBDMS_2_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-53429210d3161a8e792f | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-65bbb10c2768f3746b62 | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-b6afca3e3ac002546879 | 2015-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-0ef3797aeb5276c64c90 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-5b50453541e6f14e35be | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-5b50453541e6f14e35be | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | 2021-09-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | 2021-09-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-3142be69389832d3eb4b | 2021-09-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-65a6c4ac46a60ccd0a02 | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-75ba60e3edf4ccfcfbe0 | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-a1e091bb1f5fa6e9cbc7 | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Citric Acid Cycle |    | 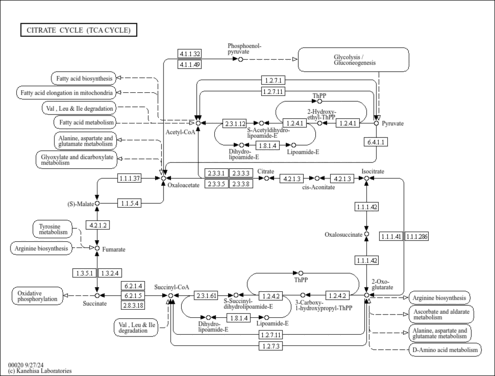 | | Urea Cycle |    | 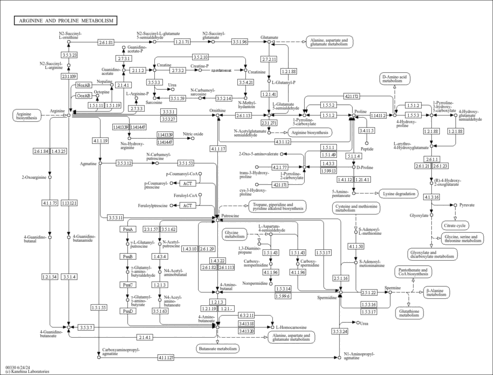 | | Threonine and 2-Oxobutanoate Degradation |    | Not Available | | Alanine Metabolism |    |  | | Primary Hyperoxaluria Type I |    | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
|---|
| Transporters | |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000595 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB023191 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 747 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C01353 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 1436647 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Carbonic acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6944 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 767 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 28976 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|


