| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-03-18 23:22:03 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2022-12-13 23:36:28 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB006159 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Citric acid |
|---|
| Description | Citric acid (citrate) is a weak tricarboxylic acid that is formed in the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In humans citric acid is produced endogenously or it may be introduced with diet, with citrus fruits being a key source. Citrate is produced by all aerobic organisms, from microbes to humans. Citrate is formed in the TCA cycle via the enzyme known as citrate synthase, which catalyzes the condensation of oxaloacetate with acetyl CoA to form citrate. Citrate then acts as the substrate for aconitase and is converted into aconitic acid. Some bacteria (notably E. coli) can produce and consume citrate internally as part of their TCA cycle, but are unable to use it as food because they lack the enzymes required to import it into the cell. Citrate has a number of biological roles in humans. In particular, it can be transported out of the mitochondria and into the cytoplasm, then broken down into acetyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis. Citrate can also acts as a signalling molecule. High concentrations of cytosolic citrate can inhibit phosphofructokinase, the catalyst of a rate-limiting step of glycolysis. Inhibition of glycolysis has been shown to suppress tumor growth in a number of animal models ( PMID: 28674429 ). Citrate is also a vital component of bone, helping to regulate the size of apatite crystals. Urinary citrate levels can be used to identify a number of disorders. Indeed urinary citrate excretion is a common tool in the differential diagnosis of kidney stones, renal tubular acidosis and it plays also a role in characterizing bone diseases such as osteoporosis (PMID 12957820 ). The secretory epithelial cells of the prostate gland of humans and other animals possess a unique citrate-related metabolic pathway regulated by testosterone and prolactin. This specialized hormone-regulated metabolic activity is responsible for the major prostate function of the production and secretion of extraordinarily high levels of citrate. The key regulatory enzymes directly associated with citrate production in the prostate cells are mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and mitochondrial aconitase. Testosterone and prolactin are involved in the regulation of the corresponding genes associated with these enzymes (PMID 12198595 ). In addition to its biological roles and endogenous production, citrate is obtained from many other sources and used in many applications. Citric acid is found in citrus fruits, most concentrated in lemons and limes, where it can comprise as much as 8% of the dry weight of the fruit. The concentrations of citric acid in citrus fruits range from 5 mM for oranges and grapefruits to 300 mM in lemons and limes. However, these values vary within species depending upon the cultivar and the circumstances in which the fruit was grown. Citric acid is a natural preservative and is also used to add an acidic (sour) taste to foods and soft drinks. Citric acid is used as an excipient in pharmaceutical preparations due to its antioxidant properties. It can be used to treat water, which makes it useful in improving the effectiveness of soaps and laundry detergents. Citric acid is also used as an acidulant in creams, gels, and liquids. The salts of citric acid (citrates) can be used as anticoagulants due to their calcium chelating ability. Intolerance to citric acid in the diet is known to exist. Altered levels of citric acid have been found to be associated with maple syrup urine disease, primary hypomagnesemia, propionic acidemia, and tyrosinemia I, which are inborn errors of metabolism. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid | ChEBI | | 2-Hydroxytricarballylic acid | ChEBI | | 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxypentane-1,5-dioic acid | ChEBI | | Citronensaeure | ChEBI | | e330 | ChEBI | | H3Cit | ChEBI | | Anhydrous citric acid | Kegg | | Citric acid anhydrous | Kegg | | 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate | Generator | | 2-Hydroxytricarballylate | Generator | | 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxypentane-1,5-dioate | Generator | | Anhydrous citrate | Generator | | Citrate anhydrous | Generator | | Citrate | Generator | | Aciletten | HMDB | | beta-Hydroxytricarballylate | HMDB | | beta-Hydroxytricarballylic acid | HMDB | | Chemfill | HMDB | | Citraclean | HMDB | | Citretten | HMDB | | Citro | HMDB | | e 330 | HMDB | | Hydrocerol a | HMDB | | Kyselina citronova | HMDB | | Suby g | HMDB | | Uro-trainer | HMDB | | Acid monohydrate, citric | HMDB | | Monohydrate, citric acid | HMDB | | Citric acid, anhydrous | HMDB | | Citric acid monohydrate | HMDB | | Uralyt u | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H8O7 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 192.12 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 192.027 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | citric acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 77-92-9 |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(=O)CC(O)(CC(O)=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H8O7/c7-3(8)1-6(13,5(11)12)2-4(9)10/h13H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H,11,12) |
|---|
| InChI Key | KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tricarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are carboxylic acids containing exactly three carboxyl groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Tricarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tricarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tricarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Hydroxy acid
- Alpha-hydroxy acid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Physiological effect | Health effect: |
|---|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | 153 °C | Not Available | | Boiling Point | 310 °C | Wikipedia | | Water Solubility | 592 mg/mL | Not Available | | logP | -1.64 | AVDEEF,A (1997) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| EI-MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-002f-9400000000-fb757b614278bb898b54 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0941000000-c310fda0e6a19bf6ae40 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0941000000-f1dfda3e9abc7cfb6b2a | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-006t-0952000000-ba3a1a80815f65afd05c | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0951000000-48857e9baebe16d9fc8d | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9531000000-b6fd7d038634694f0873 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-0593000000-b193bbba8c0cefdfe42a | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0941000000-c310fda0e6a19bf6ae40 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0941000000-f1dfda3e9abc7cfb6b2a | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-006t-0952000000-ba3a1a80815f65afd05c | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0951000000-48857e9baebe16d9fc8d | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9531000000-b6fd7d038634694f0873 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-0593000000-b193bbba8c0cefdfe42a | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0002-0941000000-573230e47a4efb1e36a5 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-002k-6900000000-d1a61a52f6efdec3101a | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, 4 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-02ib-6019300000-6d5ebea10441c6d4149a | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_1_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_2_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_2_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_2_3, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_2_4, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_3_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Citric acid, TMS_3_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-03di-2900000000-956001b034bbc0b7da96 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-000l-9100000000-55e34e2c1616942fd4f2 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-000f-9000000000-7b8be3e90a4daf85f04a | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0006-0911200000-af80d22f720facc4813a | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-014i-9000000000-6f4fedbb19821898fb22 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-03di-0900000000-8eff68ab89f7ce2262be | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0fsi-0019300000-b370c4c3dd656c8eb729 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-0006-0912100000-05e8ceb6dd97f7b9af98 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-014i-9000000000-e4b67745443c48a63bd6 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-03di-0900000000-92536abec982e0a653a0 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT (LTQ Orbitrap XL, Thermo Scientfic) , Negative | splash10-03di-0190000000-35772df08490f451d828 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0900000000-35856cc258368d13e1ff | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-3900000000-7170fdcb9749e6d6c2fb | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative | splash10-01p9-9500000000-9a502981b0a9e1ea35ad | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative | splash10-000i-9100000000-ed0c86b90e1f4966d025 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative | splash10-0a4r-9000000000-b8a975c2d639d8c91afb | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative | splash10-03di-2900000000-30970a4250098e148658 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0006-0900000000-a587dddf188152c5d7b0 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-03di-3900000000-7170fdcb9749e6d6c2fb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-01p9-9500000000-9a502981b0a9e1ea35ad | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-000i-9100000000-42a125e9128ce21bd785 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4r-9000000000-b8a975c2d639d8c91afb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-IT , negative | splash10-03di-0900000000-32af4c1bf55ea1563e53 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , negative | splash10-014i-9000000000-6f4fedbb19821898fb22 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , negative | splash10-03di-0900000000-8eff68ab89f7ce2262be | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 125 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 22.53 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 1H]-TOCSY. Unexported temporarily by An Chi on Oct 15, 2021 until json or nmrML file is generated. 2D NMR Spectrum (experimental) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Citric Acid Cycle |    | 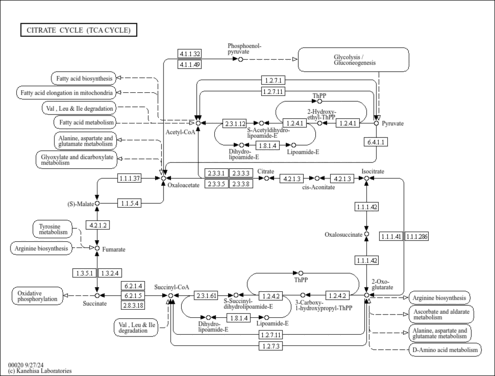 | | Transfer of Acetyl Groups into Mitochondria |    | Not Available | | Congenital lactic acidosis |    | Not Available | | Fumarase deficiency |    | Not Available | | Mitochondrial complex II deficiency |    | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
| Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit beta, mitochondrial | PDHB | 3p21.1-p14.2 | P11177 | details | | Pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 component subunit alpha, somatic form, mitochondrial | PDHA1 | Xp22.1 | P08559 | details | | Aspartate aminotransferase, mitochondrial | GOT2 | 16q21 | P00505 | details | | Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial | ACO2 | 22q13.2 | Q99798 | details | | Cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase | ACO1 | 9p21.1 | P21399 | details | | 6-phosphofructokinase, liver type | PFKL | 21q22.3 | P17858 | details | | Polycystic kidney disease 2-like 1 protein | PKD2L1 | 10q24 | Q9P0L9 | details |
|
|---|
| Transporters | Not Available |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| |
| Alien Dawg | Detected and Quantified | 6.7628 mg/g dry wt | | details | | Gabriola | Detected and Quantified | 4.415 mg/g dry wt | | details | | Island Honey | Detected and Quantified | 6.282 mg/g dry wt | | details | | Quadra | Detected and Quantified | 1.983 mg/g dry wt | | details | | Sensi Star | Detected and Quantified | 11.393 mg/g dry wt | | details | | Tangerine Dream | Detected and Quantified | 4.0481 mg/g dry wt | | details |
|
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000094 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB04272 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB030735 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00007619 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 305 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00158 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CIT |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34080 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Citric_Acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 124 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 311 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 30769 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | - Ren JG, Seth P, Ye H, Guo K, Hanai JI, Husain Z, Sukhatme VP: Citrate Suppresses Tumor Growth in Multiple Models through Inhibition of Glycolysis, the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and the IGF-1R Pathway. Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 3;7(1):4537. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04626-4. [PubMed:28674429 ]
- Caudarella R, Vescini F, Buffa A, Stefoni S: Citrate and mineral metabolism: kidney stones and bone disease. Front Biosci. 2003 Sep 1;8:s1084-106. doi: 10.2741/1119. [PubMed:12957820 ]
- Costello LC, Franklin RB: Testosterone and prolactin regulation of metabolic genes and citrate metabolism of prostate epithelial cells. Horm Metab Res. 2002 Aug;34(8):417-24. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-33598. [PubMed:12198595 ]
|
|---|
