| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-04-17 19:15:10 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-11-18 16:39:27 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB005158 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde |
|---|
| Description | (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde, also known as (2S)-2-methyl-3-oxopropanoate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds. These are carbonyl compounds with the generic formula O=C(R)C(H)C(R')=O, where R and R' can be any group (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. Within humans, (S)-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, (S)-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde can be biosynthesized from (S)-3-hydroxyisobutyric acid; which is catalyzed by the enzymes 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial and enoyl-CoA hydratase, mitochondrial. In addition, (S)-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde and L-glutamic acid can be biosynthesized from (S)-beta-aminoisobutyric acid and oxoglutaric acid; which is catalyzed by the enzyme 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, mitochondrial. In humans, (S)-methylmalonic acid semialdehyde is involved in the metabolic disorder called the 2-methyl-3-hydroxybutyryl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency pathway. 2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoic acid with configuration S at the chiral centre. (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde is expected to be in Cannabis as all living plants are known to produce and metabolize it. |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (S)-Methylmalonate semialdehyde | ChEBI | | (2S)-2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoate | HMDB | | (2S)-2-Methyl-3-oxopropanoic acid | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H6O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 102.09 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 102.0317 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-methyl-3-oxopropanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (S)-methylmalonaldehydic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 99043-16-0 |
|---|
| SMILES | C[C@@H](C=O)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H6O3/c1-3(2-5)4(6)7/h2-3H,1H3,(H,6,7)/t3-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | VOKUMXABRRXHAR-VKHMYHEASA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds. These are carbonyl compounds with the generic formula O=C(R)C(H)C(R')=O, where R and R' can be any group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 1,3-dicarbonyl compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Short-chain aldehyde
- Aldehyde
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Disposition | Source: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | logP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-8b181508e3ce65539b46 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde, 1 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-9600000000-15e42a2e09123d5f22ad | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | (S)-Methylmalonic acid semialdehyde, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0zg0-9400000000-e46caa43ec4709ce7686 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-6c1632ad1d7983990262 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-6762a2cf4db52c84495c | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-2900000000-9066dc83487b73946c99 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9200000000-8fde49823ba2083f055f | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-a320f14ddfc09e798938 | 2015-09-15 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0uk9-8900000000-0a76d84228c38b1cfe1d | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0pb9-9300000000-dd49ef94a8379e8517cd | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-4f42a2a7dc0b37e742da | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-b5c480248a004c069416 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-6de8f6b91e5efd633c28 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4r-9000000000-a0e9ace5e33e8c50915e | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine Degradation |    | 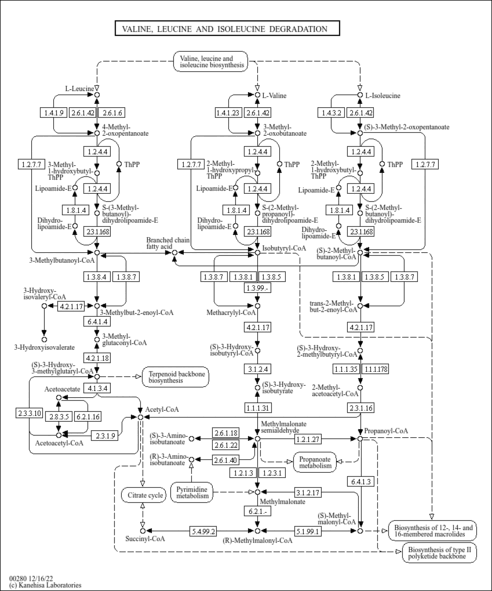 | | Propanoate Metabolism |    | 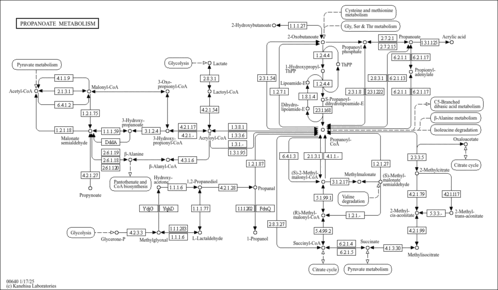 | | Beta-Ketothiolase Deficiency |    | Not Available | | 2-Methyl-3-Hydroxybutryl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency |    | Not Available | | Propionic Acidemia |    | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
| Methylmalonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase [acylating], mitochondrial | ALDH6A1 | 14q24.3 | Q02252 | details | | Aldehyde oxidase | AOX1 | 2q33 | Q06278 | details | | 4-aminobutyrate aminotransferase, mitochondrial | ABAT | 16p13.2 | P80404 | details | | 4-trimethylaminobutyraldehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH9A1 | 1q23.1 | P49189 | details | | Alpha-aminoadipic semialdehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH7A1 | 5q31 | P49419 | details | | Aldehyde dehydrogenase family 1 member A3 | ALDH1A3 | 15q26.3 | P47895 | details | | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ALDH2 | 12q24.2 | P05091 | details | | Fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase | ALDH3A2 | 17p11.2 | P51648 | details | | Aldehyde dehydrogenase X, mitochondrial | ALDH1B1 | 9p11.1 | P30837 | details | | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 | HSD17B10 | Xp11.2 | Q99714 | details | | Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | HADH | 4q22-q26 | Q16836 | details | | 3-hydroxyisobutyrate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | HIBADH | 7p15.2 | P31937 | details |
|
|---|
| Transporters | Not Available |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0002217 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB022912 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 4575365 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C06002 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CH3-MALONATE-S-ALD |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34698 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 6553 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5462303 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 27821 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|

