Showing Compound Card for MG(0:0/16:0/0:0) (CDB000797)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Created at | 2020-03-30 17:43:25 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:07:46 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CannabisDB ID | CDB000797 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cannabis Compound Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | MG(0:0/16:0/0:0) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | MG(0:0/16:0/0:0) belongs to the family of monoradyglycerols, which are glycerolipids lipids containing a common glycerol backbone to which at one fatty acyl group is attached. Their general formula is [R1]OCC(CO[R2])O[R3]. MG(0:0/16:0/0:0) is made up of one hexadecanoyl(R2). This compound is expected to be in Cannabis as all living plants are known to produce and metabolize it. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C19H38O4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Weight | 330.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 330.277 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl hexadecanoate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 1,3-dihydroxypropan-2-yl hexadecanoate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H]C(CO)(CO)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C19H38O4/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-19(22)23-18(16-20)17-21/h18,20-21H,2-17H2,1H3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | BBNYCLAREVXOSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-monoacylglycerols. These are monoacylglycerols containing a glycerol acylated at the 2-position. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Glycerolipids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Monoradylglycerols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | 2-monoacylglycerols | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ontology | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Disposition | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EI-MS/GC-MS |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MS/MS |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
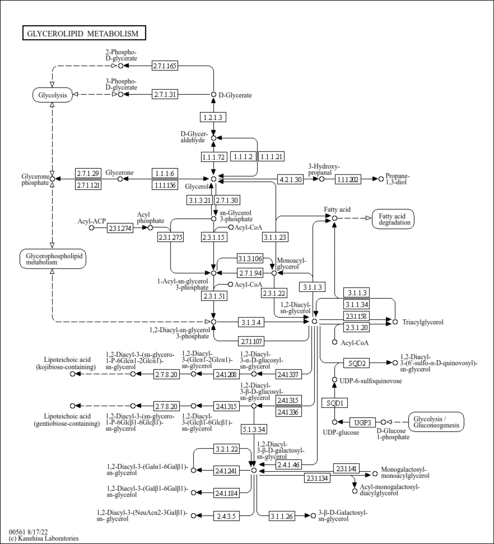
| Pathways | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protein Targets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzymes |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transporters | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metal Bindings | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Receptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0011533 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FoodDB ID | FDB003077 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 110006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG Compound ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound | 123409 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 75455 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Enzymes
- General function:
- Lipid transport and metabolism
- Specific function:
- Converts monoacylglycerides to free fatty acids and glycerol. Hydrolyzes the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol, and thereby contributes to the regulation of endocannabinoid signaling, nociperception and perception of pain (By similarity). Regulates the levels of fatty acids that serve as signaling molecules and promote cancer cell migration, invasion and tumor growth.
- Gene Name:
- MGLL
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99685
- Molecular weight:
- Not Available
- General function:
- Involved in hydrolase activity
- Specific function:
- In adipose tissue and heart, it primarily hydrolyzes stored triglycerides to free fatty acids, while in steroidogenic tissues, it principally converts cholesteryl esters to free cholesterol for steroid hormone production.
- Gene Name:
- LIPE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05469
- Molecular weight:
- 116596.715
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of diacylglycerol from 2-monoacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA. Has a preference toward monoacylglycerols containing unsaturated fatty acids in an order of C18:3 > C18:2 > C18:1 > C18:0. Plays a central role in absorption of dietary fat in the small intestine by catalyzing the resynthesis of triacylglycerol in enterocytes. May play a role in diet-induced obesity.
- Gene Name:
- MOGAT2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3SYC2
- Molecular weight:
- 38195.285
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of diacylglycerol from 2-monoacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA. Probably not involved in absorption of dietary fat in the small intestine (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- MOGAT1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96PD6
- Molecular weight:
- 38812.19
- General function:
- Involved in transferase activity, transferring acyl groups other than amino-acyl groups
- Specific function:
- Catalyzes the formation of diacylglycerol from 2-monoacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA. Also able to catalyze the terminal step in triacylglycerol synthesis by using diacylglycerol and fatty acyl-CoA as substrates. Has a preference toward palmitoyl-CoA and oleoyl-CoA. May be involved in absorption of dietary fat in the small intestine by catalyzing the resynthesis of triacylglycerol in enterocytes.
- Gene Name:
- MOGAT3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q86VF5
- Molecular weight:
- 38729.84
- General function:
- Involved in acid phosphatase activity
- Specific function:
- Hydrolyzes lysophosphatidic acid to monoacylglycerol.
- Gene Name:
- ACP6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NPH0
- Molecular weight:
- 48853.955
- General function:
- Involved in NAD+ kinase activity
- Specific function:
- Lipid kinase that can phosphorylate both monoacylglycerol and diacylglycerol to form lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and phosphatidic acid (PA), respectively. Does not phosphorylate sphingosine. Overexpression increases the formation and secretion of LPA, resulting in transactivation of EGFR and activation of the downstream MAPK signaling pathway, leading to increased cell growth
- Gene Name:
- AGK
- Uniprot ID:
- Q53H12
- Molecular weight:
- 47136.8
- General function:
- Involved in catalytic activity
- Specific function:
- Choline-specific glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase. The preferred substrate may be lysosphingomyelin (By similarity). Hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) to form monoacylglycerol and phosphorylcholine but not lysophosphatidic acid, showing it has a lysophospholipase C activity. Has a preference for LPC with short (12:0 and 14:0) or polyunsaturated (18:2 and 20:4) fatty acids. Also hydrolyzes glycerophosphorylcholine and sphingosylphosphorylcholine efficiently. Hydrolyzes the classical substrate for phospholipase C, p-nitrophenyl phosphorylcholine in vitro, while it does not hydrolyze the classical nucleotide phosphodiesterase substrate, p-nitrophenyl thymidine 5'-monophosphate. Does not hydrolyze diacyl phospholipids such as phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidic acid.
- Gene Name:
- ENPP6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6UWR7
- Molecular weight:
- 50240.625