| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-03-19 00:33:41 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:07:24 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB000374 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Gamma-linolenic acid |
|---|
| Description | Gamma-Linolenic acid is also known as 18:3 (N-6), gamolenic acid or gamma-linolensaeure. It is an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) also referred to as 9,12-octadecatrienoic acid (cis-6, cis-9, cis-12- octadecatrienoic acid). It belongs to the class of organic compounds known as lineolic acids and derivatives. These are derivatives of lineolic acid. Lineolic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 18 carbon long fatty acid, with two CC double bonds at the 9- and 12-positions. gamma-Linolenic acid is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble in water, and relatively neutral. It is found largely in human milk and other botanical sources. Gamma-Linolenic acid is found in varying amounts in edible hemp seeds, oats, barley and spirulina. Gamma-linolenic acid is one of the unsaturated fatty acids found in the oil of cannabis seeds (PMID: 6991645 ). Gamolenic acid is also found in some fungal sources and is present naturally in the form of triglycerides. Gamolenic acid may be found in over-the-counter dietary supplements. Gamma-Linolenic acid is an omega-6 fatty acid produced in the body as the delta 6-desaturase metabolite of linoleic acid. It is converted into dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, a biosynthetic precursor of monoenoic prostaglandins such as Prostaglandin E1(PGE1). Evening primrose oil, containing 7-14% gamma-linolenic acid, has been investigated for clinical use in menopausal syndrome, diabetic neuropathy, breast pain (PMID: 27083549 ) and eczema. It has been questioned if evening primrose oil, containing gamma-linolenic acid, helped alleviate atopic eczema (PMID: 14670851 ). However, its effectiveness in treating eczema was demonstrated in a study where the topical application of borage seed oil (with higher concentrations of gamma linolenic acid than evening primrose oil) reduced symptoms of atopic dermatitis in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (PMID: 18078406 ).Various clinical indications of gamolenic acid have been studied, including rheumatoid arthritis, atopic eczema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, asthma, premenstrual syndrome, cardiovascular disease, ulcerative colitis, ADHD, cancer, osteoporosis, diabetic neuropathy, and insomnia ( PMID: 27083549 ; PMID: 27083549 ). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (6,9,12)-Linolenic acid | ChEBI | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | 18:3 (N-6) | ChEBI | | 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | 6-cis,9-cis,12-cis-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | all-cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | C18:3 (N-6) | ChEBI | | C18:3, N-6,9,12 all-cis | ChEBI | | cis-Delta(6,9,12)-Octadecatrienoic acid | ChEBI | | gamma-Linolensaeure | ChEBI | | Gamoleic acid | ChEBI | | Gamolenic acid | ChEBI | | GLA | ChEBI | | Octadeca-6,9,12-triensaeure | ChEBI | | (6,9,12)-Linolenate | Generator | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | 6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | 6-cis,9-cis,12-cis-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | all-cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-delta(6,9,12)-Octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-Δ(6,9,12)-octadecatrienoate | Generator | | cis-Δ(6,9,12)-octadecatrienoic acid | Generator | | g-Linolensaeure | Generator | | Γ-linolensaeure | Generator | | Gamoleate | Generator | | Gamolenate | Generator | | g-Linolenate | Generator | | g-Linolenic acid | Generator | | gamma-Linolenate | Generator | | Γ-linolenate | Generator | | Γ-linolenic acid | Generator | | 6(Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6(Z),9(Z),12(Z)-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | 6,9,12-all-cis-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6,9,12-all-cis-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | 6Z,9Z,12Z-Octadecatrienoate | HMDB | | 6Z,9Z,12Z-Octadecatrienoic acid | HMDB | | gamma-Llnolenic acid | HMDB | | Ligla | HMDB | | Acid, gamma-linolenic | HMDB | | Acid, gamolenic | HMDB | | gamma Linolenic acid | HMDB | | FA(18:3(6Z,9Z,12Z)) | HMDB | | FA(18:3n6) | HMDB | | Linolenate | HMDB | | gamma-Linolenic acid | KEGG | | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | (Z,Z,Z)-6,9,12-Octatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | cis,cis,cis-6,9,12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank | | cis-6,cis-9,cis-12-Octadecatrienoic acid | PhytoBank |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C18H30O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 278.43 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 278.2246 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (6Z,9Z,12Z)-octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | gamma linolenic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 506-26-3 |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C18H30O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h6-7,9-10,12-13H,2-5,8,11,14-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12- |
|---|
| InChI Key | VZCCETWTMQHEPK-QNEBEIHSSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as lineolic acids and derivatives. These are derivatives of lineolic acid. Lineolic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 18 carbon long fatty acid, with two CC double bonds at the 9- and 12-positions. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Lineolic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Lineolic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Octadecanoid
- Long-chain fatty acid
- Fatty acid
- Unsaturated fatty acid
- Straight chain fatty acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Biological role: Industrial application: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | Not Available | Not Available | | logP | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| EI-MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-00nf-9200000000-cf911df79059a750cb2a | 2015-03-01 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, 1 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-005c-9800000000-7b6e7a36b048f5ed69bd | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00b9-9300000000-254ecb989081fdc719d2 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-005c-9800000000-7b6e7a36b048f5ed69bd | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9650000000-eec5566c0f0f90bf0049 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, 1 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-007c-9431000000-b239852c91e567668780 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Gamma-linolenic acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 20V, Negative | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 30V, Negative | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 10V, Negative | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF , Negative | splash10-005l-0902100000-6fc8730bd28daa779b66 | 2017-08-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-143e6ddfa05656a4c4da | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 30V, Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-63bf7d731625d5577978 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-fbc4e202a8b26c91dc9e | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - ESI-TOF , Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-b56d00321ab0921fe7b7 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-dcae4273443fd52bbb03 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-TOF , negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-143e6ddfa05656a4c4da | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-TOF , negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-TOF , negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-63bf7d731625d5577978 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 10V, positive | splash10-004i-0090000000-370b301c8afc435a0ce1 | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 20V, positive | splash10-003s-9850000000-54163d6f895368b9032c | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF 40V, positive | splash10-001i-9000000000-e6cdb81ac5675944be82 | 2020-07-21 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-003s-9750000000-d1947011d4fc6a28a135 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 30V, Positive | splash10-004i-0090000000-0b9ba563ad074fe141e8 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-0090000000-370b301c8afc435a0ce1 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01t9-0190000000-6b136607b48b31667801 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01q9-4790000000-5046458d5d3e3c228518 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05mo-8930000000-852d50a19eb0b0df729b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0090000000-ab643cae783eb66bf131 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0059-1090000000-abce276de392be9d7d3f | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9230000000-40a41feed498373e54d2 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, H2O, predicted) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Alpha Linolenic Acid and Linoleic Acid Metabolism |    | 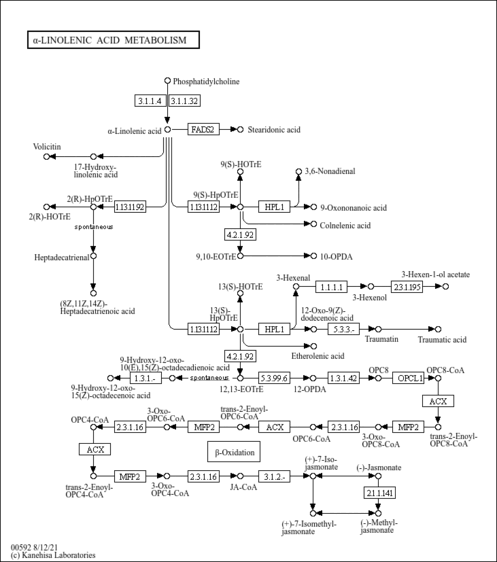 |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
|---|
| Transporters | Not Available |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | |
|---|
| Receptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0003073 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB13854 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB002943 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001226 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 4444436 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C06426 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | CPD-8117 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 48234 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Gamma-Linolenic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 386 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 5280933 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 28661 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | - Turner CE, Elsohly MA, Boeren EG: Constituents of Cannabis sativa L. XVII. A review of the natural constituents. J Nat Prod. 1980 Mar-Apr;43(2):169-234. doi: 10.1021/np50008a001. [PubMed:6991645 ]
- Sergeant S, Rahbar E, Chilton FH: Gamma-linolenic acid, Dihommo-gamma linolenic, Eicosanoids and Inflammatory Processes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Aug 15;785:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 12. [PubMed:27083549 ]
- Williams HC: Evening primrose oil for atopic dermatitis. BMJ. 2003 Dec 13;327(7428):1358-9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7428.1358. [PubMed:14670851 ]
- Kanehara S, Ohtani T, Uede K, Furukawa F: Clinical effects of undershirts coated with borage oil on children with atopic dermatitis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Dermatol. 2007 Dec;34(12):811-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00391.x. [PubMed:18078406 ]
|
|---|
