| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Created at | 2020-03-18 23:27:36 UTC |
|---|
| Updated at | 2020-12-07 19:07:12 UTC |
|---|
| CannabisDB ID | CDB000176 |
|---|
| Secondary Accession Numbers | Not Available |
|---|
| Cannabis Compound Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|
| Description | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoate or 4-carboxyphenol, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives are compounds containing a hydroxybenzoic acid (or a derivative), which is a benzene ring bearing a carboxyl and a hydroxyl group. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a neutral compound with a nutty and phenolic taste. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid exists in all living species, from bacteria to humans. In humans, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid is involved in ubiquinone biosynthesis. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is found in highest concentrations in red huckleberries, corianders, and garden onions and in lower concentrations in soybeans, rye bread, and almonds. 4-hydroxybenzoic acid has also been detected in sour cherries, common beans, wild carrots, common oregano, and soft-necked garlics. This could make 4-hydroxybenzoic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is also found in cannabis plants (PMID:6991645 ). 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid esters, known as parabens, are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid has estrogenic activity and stimulated the growth of breast cancer cell lines (PMID: 16021681 ). It can be found in Escherichia coli as part of the ubiquinone pathway. In the first step of this pathway, chorismate lyase transforms chorismate into 4-hydroxybenzoate and pyruvate (PMID 1644758 ). In Pseudomonas sp., 4-hydroxybenzoate and chloride are produced when the enzyme 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase acts on the halide bond of 4-chlorobenzoate with H2O (PMID: 6497878 ). |
|---|
| Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 4-Carboxyphenol | ChEBI | | p-HYDROXYBENZOIC ACID | ChEBI | | p-Salicylic acid | ChEBI | | Hydroxybenzoic acid | Kegg | | Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid | Kegg | | p-HYDROXYBENZOate | Generator | | p-Salicylate | Generator | | Hydroxybenzoate | Generator | | Hydroxybenzenecarboxylate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxybenzoate | Generator | | 4-Hydroxy-benzoate | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxy-benzoesaeure | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxy-benzoic acid | HMDB | | p-Carboxyphenol | HMDB | | p-Hydroxy-benzoate | HMDB | | p-Hydroxy-benzoic acid | HMDB | | Paraben-acid | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, calcium salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, dilithium salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, disodium salt | HMDB | | Para-hydroxybenzoic acid | HMDB | | Sodium p-hydroxybenzoate tetrahydrate | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, copper(2+)(1:1) salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, dipotassium salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, monopotassium salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, monosodium salt | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, monosodium salt, 11C-labeled | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzene carboxylic acid | HMDB | | p-Hydroxyl benzoic acid | HMDB | | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C7H6O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Weight | 138.12 |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Molecular Weight | 138.0317 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 4-hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | P-hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 99-96-7 |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C7H6O3/c8-6-3-1-5(2-4-6)7(9)10/h1-4,8H,(H,9,10) |
|---|
| InChI Key | FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | Belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives are compounds containing a hydroxybenzoic acid (or a derivative), which is a benzene ring bearing a carboxyl and a hydroxyl groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzoic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Hydroxybenzoic acid
- Benzoic acid
- Benzoyl
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Ontology |
|---|
|
| Physiological effect | Health effect: |
|---|
| Disposition | Route of exposure: Source: Biological location: |
|---|
| Role | Industrial application: |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value | Reference |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | Not Available | | Water Solubility | 5 mg/mL | Not Available | | logP | 1.58 | HANSCH,C ET AL. (1995) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | [] |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| EI-MS/GC-MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| EI-MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-00dr-6900000000-71548845dbf99346758d | 2015-03-01 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, 2 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-01b9-0490000000-89473836b0071542185e | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00xu-2890000000-dd5367ba838ccd5b29d8 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, 2 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9540000000-11db590137f79b7a32bf | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, 2 TMS, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00xu-3890000000-7e553522b6ec5c075e25 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00dr-5900000000-9b1d88421f1e1ded16f9 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9700000000-a9bb4b71d8b23a56ca67 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-0079-6900000000-617d58eb059c1e918ca0 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00dr-4900000000-97bfa38b0d6bc152d470 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00dr-7900000000-290af590b1fc44a86969 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-01b9-0490000000-d6001fb50397705d3e0b | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-01b9-0490000000-89473836b0071542185e | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00xu-2890000000-dd5367ba838ccd5b29d8 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00di-9540000000-11db590137f79b7a32bf | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00xu-3890000000-7e553522b6ec5c075e25 | Spectrum | | GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, GC-MS Spectrum | splash10-00xu-2980000000-0ba0ea7d63bd7fff3b22 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0079-5900000000-fcde26d72ca8445dff7e | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, 2 TMS, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00xu-7950000000-cc553d409cc2a872749d | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, non-derivatized, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, TMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, TMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, TBDMS_1_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, TBDMS_1_2, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, TBDMS_2_1, Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| MS/MS | | Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-000f-9400000000-9fb9f8fbd7cf90a88604 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-f5d09d09184f72ec3bd7 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Negative (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-d31cea608d0764edf5d0 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - EI-B (HITACHI M-68) , Positive | splash10-00dr-5900000000-9b1d88421f1e1ded16f9 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - EI-B (HITACHI M-60) , Positive | splash10-00di-9700000000-3ac766249fee4c68b8f4 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - EI-B (HITACHI M-80) , Positive | splash10-0079-6900000000-4e15a4102e0b3bc8ddce | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4r-9800000000-9e7208bfb79f9cca336b | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-1ed6d8123d44d126ed64 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-63a0e9c65e315bb89281 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-a8befcaa45eced4a9a51 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-26788d399f2b459abc21 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive | splash10-0072-6900000000-ba06f5c422d59cd10cea | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Positive | splash10-0002-9100000000-193fd4eb0cf324fb3abc | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF (UPLC Q-Tof Premier, Waters) , Negative | splash10-0006-9200000000-c834f7be13341f3e19b8 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - DI-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-00di-0900000000-4f58e660923e896589a3 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4r-9800000000-9e7208bfb79f9cca336b | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-1ed6d8123d44d126ed64 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-e80d9637393e63e2d07c | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-a8befcaa45eced4a9a51 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0079-0900000000-6351b89d53d1742a1fbb | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-1900000000-bdd873f3d1dc0f2af556 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00fu-9400000000-37262c1edda5dec21a19 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-3900000000-fcd512c9827982e7c9aa | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000f-9600000000-36013030005316a50fab | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9100000000-5efa05442f95e2900559 | 2016-09-12 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| NMR | | Type | Description | | View |
|---|
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 90 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 25.16 MHz, D2O, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, DMSO, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, DMSO, experimental) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 1H]-TOCSY. Unexported temporarily by An Chi on Oct 15, 2021 until json or nmrML file is generated. 2D NMR Spectrum (experimental) | | Spectrum | | 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Pathways |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | Ubiquinone Biosynthesis |    | 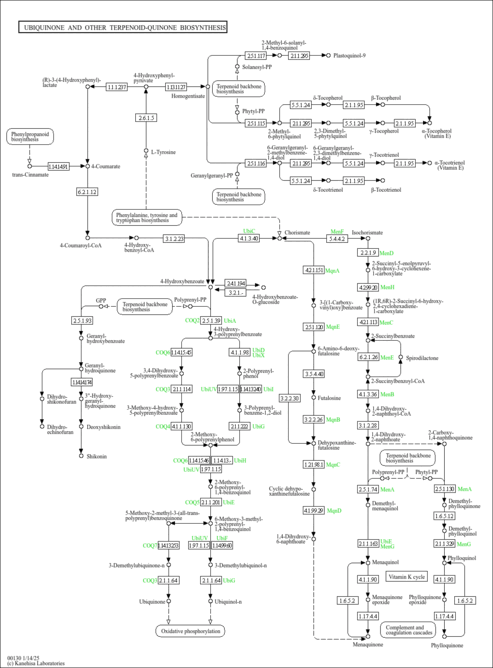 |
|
|---|
| Protein Targets |
|---|
| Enzymes | |
|---|
| Transporters | Not Available |
|---|
| Metal Bindings | Not Available |
|---|
| Receptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Transcriptional Factors | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations Data |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000500 |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB04242 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer Compound ID | 418 |
|---|
| FoodDB ID | FDB010508 |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00000856 |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 132 |
|---|
| KEGG Compound ID | C00156 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | 4-hydroxybenzoate |
|---|
| BiGG ID | 34069 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | 4-Hydroxybenzoic_acid |
|---|
| METLIN ID | 5486 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound | 135 |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 30763 |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| General References | - Turner CE, Elsohly MA, Boeren EG: Constituents of Cannabis sativa L. XVII. A review of the natural constituents. J Nat Prod. 1980 Mar-Apr;43(2):169-234. doi: 10.1021/np50008a001. [PubMed:6991645 ]
- Pugazhendhi D, Pope GS, Darbre PD: Oestrogenic activity of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (common metabolite of paraben esters) and methylparaben in human breast cancer cell lines. J Appl Toxicol. 2005 Jul-Aug;25(4):301-9. doi: 10.1002/jat.1066. [PubMed:16021681 ]
- Nichols BP, Green JM: Cloning and sequencing of Escherichia coli ubiC and purification of chorismate lyase. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5309-16. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5309-5316.1992. [PubMed:1644758 ]
- Muller R, Thiele J, Klages U, Lingens F: Incorporation of [18O]water into 4-hydroxybenzoic acid in the reaction of 4-chlorobenzoate dehalogenase from pseudomonas spec. CBS 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):178-82. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90933-1. [PubMed:6497878 ]
|
|---|
