| Identification |
|---|
| HMDB Protein ID
| CDBP05347 |
| Secondary Accession Numbers
| Not Available |
| Name
| Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III |
| Description
| Not Available |
| Synonyms
|
- eIF-4A-III
- eIF4A-III
- ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX48
- ATP-dependent RNA helicase eIF4A-3
- DEAD box protein 48
- Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-like NUK-34
- Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A isoform 3
- Nuclear matrix protein 265
- NMP 265
- hNMP 265
|
| Gene Name
| EIF4A3 |
| Protein Type
| Enzyme |
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| General Function
| Not Available |
| Specific Function
| ATP-dependent RNA helicase. Component of a splicing-dependent multiprotein exon junction complex (EJC) deposited at splice junction on mRNAs. The EJC is a dynamic structure consisting of a few core proteins and several more peripheral nuclear and cytoplasmic associated factors that join the complex only transiently either during EJC assembly or during subsequent mRNA metabolism. Core components of the EJC, that remains bound to spliced mRNAs throughout all stages of mRNA metabolism, functions to mark the position of the exon-exon junction in the mature mRNA and thereby influences downstream processes of gene expression including mRNA splicing, nuclear mRNA export, subcellular mRNA localization, translation efficiency and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Constitutes at least part of the platform anchoring other EJC proteins to spliced mRNAs. Its RNA-dependent ATPase and RNA-helicase activities are induced by CASC3, but abolished in presence of the MAGOH/RBM8A heterodimer, thereby trapping the ATP-bound EJC core onto spliced mRNA in a stable conformation. The inhibition of ATPase activity by the MAGOH/RBM8A heterodimer increases the RNA-binding affinity of the EJC. Involved in translational enhancement of spliced mRNAs after formation of the 80S ribosome complex. Binds spliced mRNA in sequence-independent manner, 20-24 nucleotides upstream of mRNA exon-exon junctions. Shows higher affinity for single-stranded RNA in an ATP-bound core EJC complex than after the ATP is hydrolyzed.
|
| GO Classification
|
| Biological Process |
| nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, nonsense-mediated decay |
| mRNA transport |
| negative regulation of translation |
| mRNA splicing, via spliceosome |
| nuclear-transcribed mRNA poly(A) tail shortening |
| positive regulation of translation |
| rRNA processing |
| cytokine-mediated signaling pathway |
| Cellular Component |
| cytosol |
| catalytic step 2 spliceosome |
| nuclear speck |
| exon-exon junction complex |
| Molecular Function |
| ATP-dependent RNA helicase activity |
| poly(A) RNA binding |
| ATP binding |
|
| Cellular Location
|
Not Available
|
| Pathways
|
| Name | SMPDB/Pathwhiz | KEGG | | RNA transport | Not Available | 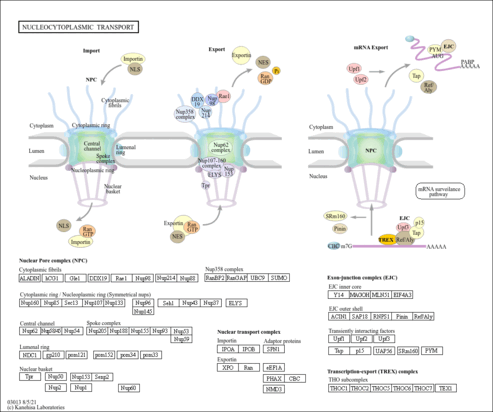 | | mRNA surveillance pathway | Not Available | 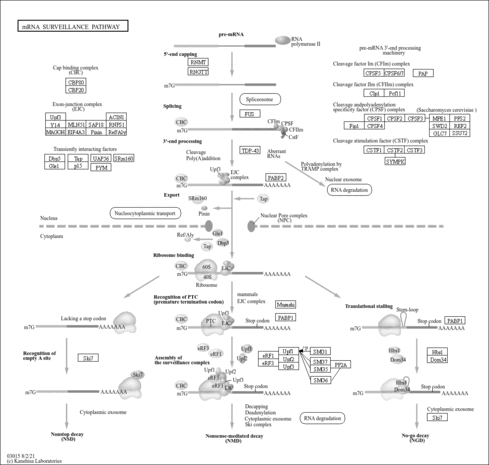 | | Spliceosome | Not Available | 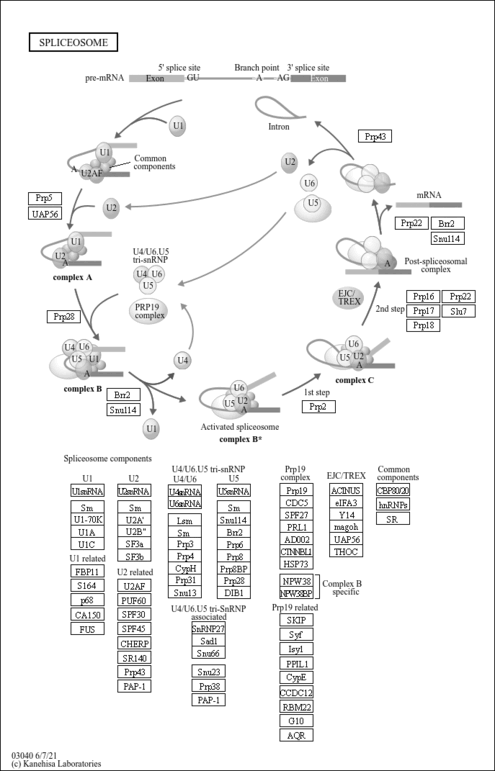 |
|
| Gene Properties |
|---|
| Chromosome Location
| 17 |
| Locus
| 17q25.3 |
| SNPs
| Not Available |
| Gene Sequence
|
Not Available
|
| Protein Properties |
|---|
| Number of Residues
| Not Available |
| Molecular Weight
| 46870.62 |
| Theoretical pI
| 6.72 |
| Pfam Domain Function
|
Not Available |
| Signals
|
Not Available
|
|
Transmembrane Regions
|
Not Available
|
| Protein Sequence
|
>gi|7661920|ref|NP_055555.1| eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III [Homo sapiens]
MATTATMATSGSARKRLLKEEDMTKVEFETSEEVDVTPTFDTMGLREDLLRGIYAYGFEK
PSAIQQRAIK
|
| External Links |
|---|
| GenBank ID Protein
| Not Available |
| UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot ID
| P38919 |
| UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Entry Name
| Not Available |
| PDB IDs
|
|
| GenBank Gene ID
| Not Available |
| GeneCard ID
| Not Available |
| GenAtlas ID
| Not Available |
| HGNC ID
| HGNC:18683 |
| References |
|---|
| General References
| Not Available |


